What Is Pgvector?
pgvector is an open source PostgreSQL extension that adds support for vector data types and vector-based indexing. It allows users to store, query, and search high-dimensional vector embeddings directly in a PostgreSQL database, integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning workflows within SQL-based environments.
By providing efficient similarity search capabilities, pgvector bridges the gap between traditional relational data and modern unstructured data representations like embeddings from natural language models. The extension handles a large number of vectors, offering specialized indexing methods such as the approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search using IVFFlat.
This enables rapid similarity searches required for AI-powered applications, such as recommendation engines or semantic text retrieval, without leaving the comfort of a relational database. By treating vectors as the most important element with their own data type and functions, pgvector expands what can be achieved using PostgreSQL alone.
What Is Hybrid Search?
Hybrid search combines vector-based similarity search with traditional keyword or metadata filtering to deliver highly relevant results. While vector search leverages embeddings to find items that are semantically similar, it often lacks precision when users need to constrain their results using structured attributes or keywords.
Hybrid search addresses this gap by enabling both types of queries in a single operation, providing a more refined and context-aware retrieval experience. In this model, a typical query might first filter a dataset based on categorical information or keywords, then apply vector similarity to rank or further narrow the results.
This approach is valuable when dealing with real-world data, where both the semantic meaning and structured attributes are important. Tools like pgvector make hybrid search feasible within PostgreSQL, allowing developers to combine modern AI-powered methods with classic SQL querying.
This is part of a series of articles about vector database
Benefits of Using Pgvector for Hybrid Search
Using pgvector for hybrid search in PostgreSQL environments offers several practical advantages:
- Single-platform integration: pgvector allows teams to manage both structured data and vector embeddings in the same PostgreSQL instance. This eliminates the need for separate vector databases or synchronization layers.
- Simplified query logic: Hybrid search queries can be expressed using standard SQL syntax, combining traditional filters (WHERE, JOIN, etc.) with vector similarity functions (<->). This makes complex queries more maintainable and easier to debug.
- Reduced latency: Performing vector and structured filtering in one query minimizes data transfer and processing overhead. It keeps all computation inside the database, improving performance for real-time applications.
- Custom indexing strategies: pgvector supports indexing methods like IVFFlat, which accelerates approximate nearest neighbor search. These indexes can be tuned for specific workloads, balancing accuracy and speed.
- Scalable and production-ready: Built on PostgreSQL, pgvector inherits a mature, stable foundation with transactional integrity, role-based access control, and horizontal scaling options via extensions like Citus.
- Flexible scoring and ranking: Results can be ordered using custom scoring formulas that combine similarity metrics with domain-specific ranking logic, such as popularity, recency, or user-specific weights.
- Ecosystem compatibility: pgvector works with PostgreSQL-compatible tools and ORMs, making it easier to adopt in existing systems without major architectural changes.
Use Cases of Pgvector Hybrid Search
eCommerce Product Discovery
eCommerce sites face the challenge of guiding users to products they might want or need. Hybrid search with pgvector makes it possible to combine keyword searches like “blue running shoes” with semantic matching across product descriptions, user reviews, and images. For instance, users can filter by price, availability, or brand while seeing products similar to others they have viewed or purchased, even if they don’t share exact keywords.
The addition of vector search ensures the discovery of visually or descriptively similar products, supporting features such as “more like this” recommendations. Combined filtering and similarity ranking deliver better product curation, lower bounce rates, and higher user satisfaction.
Document Retrieval in Knowledge Bases
In large knowledge bases or documentation portals, finding the right piece of information can be challenging due to varied terminology, document formats, or organizational silos. Hybrid search with pgvector enables users to filter by document type, author, or date, while also harnessing vector embeddings to find content semantically related to a user’s query. This approach bridges gaps between keywords and actual user intent.
For enterprises, this capability reduces time spent searching and improves knowledge discovery. Team members can locate conceptually related guides, policies, or troubleshooting steps without needing to know exact phrases.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) architectures combine vector search with generative AI to improve responses with factual accuracy and context. With pgvector, a RAG pipeline can search a PostgreSQL database of document embeddings to retrieve the most relevant passages, which are then fed into a language model for context-aware generation. Hybrid search refines the retrieval step, allowing constraints such as author, publication date, or source type to be enforced.
This approach improves the factuality and relevance of generated outputs, as the underlying context comes from semantically similar and filtered sources. RAG augmented with pgvector is increasingly used in chatbots, virtual assistants, and enterprise AI solutions where grounding responses in verifiable data is critical.
Enterprise Search Applications
Organizations often amass vast volumes of structured and unstructured data (emails, reports, contracts, etc.). Hybrid search with pgvector equips internal search engines to surface relevant results across heterogeneous document types by marrying SQL-based filtering (department, author, date) with vector-driven semantic ranking. This improves the search experience for employees, ensuring they retrieve not only exact matches but also contextually relevant documents.
By keeping metadata and embeddings together in PostgreSQL, enterprises maintain robust governance and simplified access control. IT teams can leverage familiar backup, monitoring, and disaster recovery workflows while building advanced search capabilities. The result is more efficient information retrieval, improved productivity, and secure knowledge management.
Related content: Read our guide to Pgvector performance (coming soon)
Tips from the expert

Perry Clark
Professional Services Consultant
Perry Clark is a seasoned open source consultant with NetApp. Perry is passionate about delivering high-quality solutions and has a strong background in various open source technologies and methodologies, making him a valuable asset to any project.
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better apply and optimize pgvector hybrid search in PostgreSQL:
- Materialize hybrid scores for frequent queries: For high-traffic endpoints, precompute and cache hybrid scores in materialized views or separate summary tables. This reduces CPU overhead from real-time fusion and speeds up query responses, especially for RAG pipelines and enterprise search.
- Segment ANN indexes by metadata constraints: Instead of a single IVFFlat or HNSW index, partition the dataset and maintain separate indexes for different categories, user roles, or time ranges. This reduces candidate sets and improves hybrid search latency without sacrificing recall.
- Enforce index-only scans via computed vector similarity columns: To push similarity scoring deeper into the index access path, store precomputed similarity metrics as virtual/generated columns and index those. This enables index-only scans in certain hybrid search patterns, improving performance.
- Optimize vector index parameters dynamically: Adjust IVFFlat/HNSW parameters (e.g., ef_search, ef_construction, nlist) based on query context or workload profile. Implement these as session-level settings or route queries through different PostgreSQL roles with tuned configs.
- Use embedding quantization for large-scale vector storage: If storage becomes a bottleneck, apply dimensionality reduction (e.g., PCA) or quantization techniques (e.g., product quantization) to compress embeddings before inserting. This allows storing millions of vectors efficiently without large disk footprints.
Tutorial: Hybrid Search with PostgreSQL and Pgvector
This section walks through a practical implementation of hybrid search using PostgreSQL and the pgvector extension. The setup combines full-text search and vector similarity to improve result ranking in a searchable dataset.
- Schema and extension setup
First, ensure pgvector is installed in your PostgreSQL instance:
|
1 |
CREATE EXTENSION vector; |
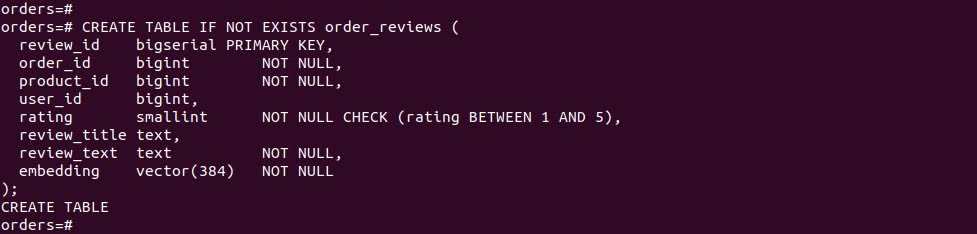
Next, define a table to hold your searchable items. In this example, we store product descriptions along with their vector embeddings:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS order_reviews ( review_id bigserial PRIMARY KEY, order_id bigint NOT NULL, product_id bigint NOT NULL, user_id bigint, rating smallint NOT NULL CHECK (rating BETWEEN 1 AND 5), review_title text, review_text text NOT NULL, embedding vector(384) NOT NULL); |
- Data generation and embedding
For demonstration, synthetic order review and review title are generated using GPT Model. You can download the dataset using this link. . Embeddings are computed using the
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 |
multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1 model from sentence-transformers: from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer from pgvector.psycopg2 import register_vector from psycopg2.extras import execute_values import psycopg2 import pandas as pd import numpy as np from tqdm import tqdm # ----------------------------- # Database config # ----------------------------- DB = dict( dbname="orders", user="my_user", password="yyooal8h", host="127.0.0.1", port=5432, ) CSV_PATH = "/tmp/order_reviews_sample_5000.csv" # ----------------------------- # Main function # ----------------------------- def main(): print(f"Loading CSV from {CSV_PATH} ...") df = pd.read_csv(CSV_PATH) print(f"Loaded {len(df)} rows.") # Load embedding model (384-dim) print("Loading SentenceTransformer model (multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1)...") model = SentenceTransformer("multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1") print("Model loaded.") # Connect to PostgreSQL conn = psycopg2.connect(**DB) conn.autocommit = True cur = conn.cursor() register_vector(cur) # Insert in batches BATCH = 500 total = len(df) inserted = 0 with tqdm(total=total, desc="Inserting", unit="rows") as pbar: for start in range(0, total, BATCH): end = min(start + BATCH, total) batch = df.iloc[start:end] # Compute embeddings for review_text embeddings = model.encode( batch["review_text"].tolist(), convert_to_numpy=True ).astype(np.float32) rows = [ ( int(batch.iloc[i]["order_id"]), int(batch.iloc[i]["product_id"]), int(batch.iloc[i]["user_id"]), int(batch.iloc[i]["rating"]), batch.iloc[i]["review_title"], batch.iloc[i]["review_text"], embeddings[i], ) for i in range(len(batch)) ] execute_values( cur, """ INSERT INTO order_reviews (order_id, product_id, user_id, rating, review_title, review_text, embedding) VALUES %s """, rows, template="(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)", ) inserted += len(batch) pbar.update(len(batch)) cur.close() conn.close() print(f"Done! Inserted {inserted} rows into order_reviews.") # ----------------------------- # Entry Point # ----------------------------- if __name__ == "__main__": main() |
You will need to install the following python libraries in order to execute the above code. Please use איק following command:
|
1 2 |
pip install -U pip setuptools wheel pip install sentence-transformers numpy psycopg2-binary pgvector tqdm |
- Indexing
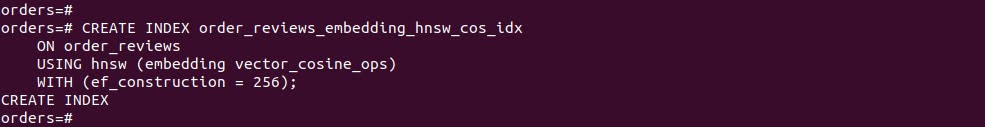
To enable fast search, create two indexes:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
-- Full-text search index on review_text CREATE INDEX order_reviews_review_text_fts_idx ON order_reviews USING GIN (to_tsvector('english', review_text)); -- Vector similarity index using HNSW (cosine distance) CREATE INDEX order_reviews_embedding_hnsw_cos_idx ON order_reviews USING hnsw (embedding vector_cosine_ops) WITH (ef_construction = 256); |
- Full-text and vector-only searches
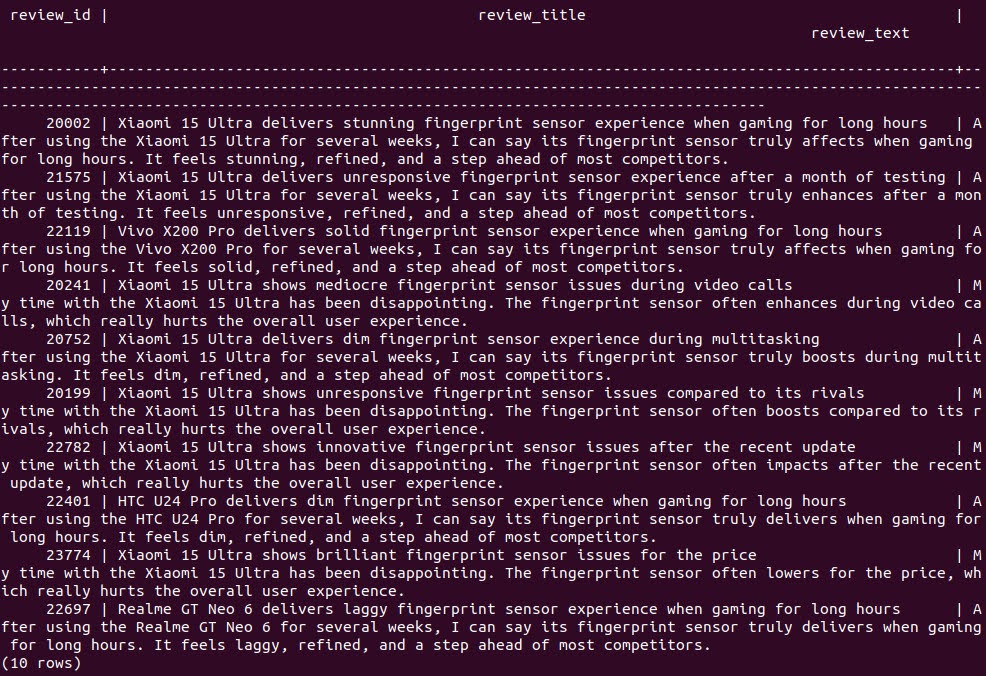
You can query for relevant items using either method alone. For vector search:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
WITH q AS ( SELECT embedding AS v FROM order_reviews ORDER BY review_id LIMIT 1 ) SELECT review_id, review_title, review_text FROM order_reviews, q ORDER BY order_reviews.embedding <-> q.v LIMIT 10; |
And for full-text search:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
SELECT review_id, review_title, review_text, ts_rank_cd( to_tsvector('english', review_text), plainto_tsquery('english', 'camera') ) AS rank FROM order_reviews WHERE plainto_tsquery('english', 'camera') @@ to_tsvector('english', review_text) ORDER BY rank DESC LIMIT 10; |
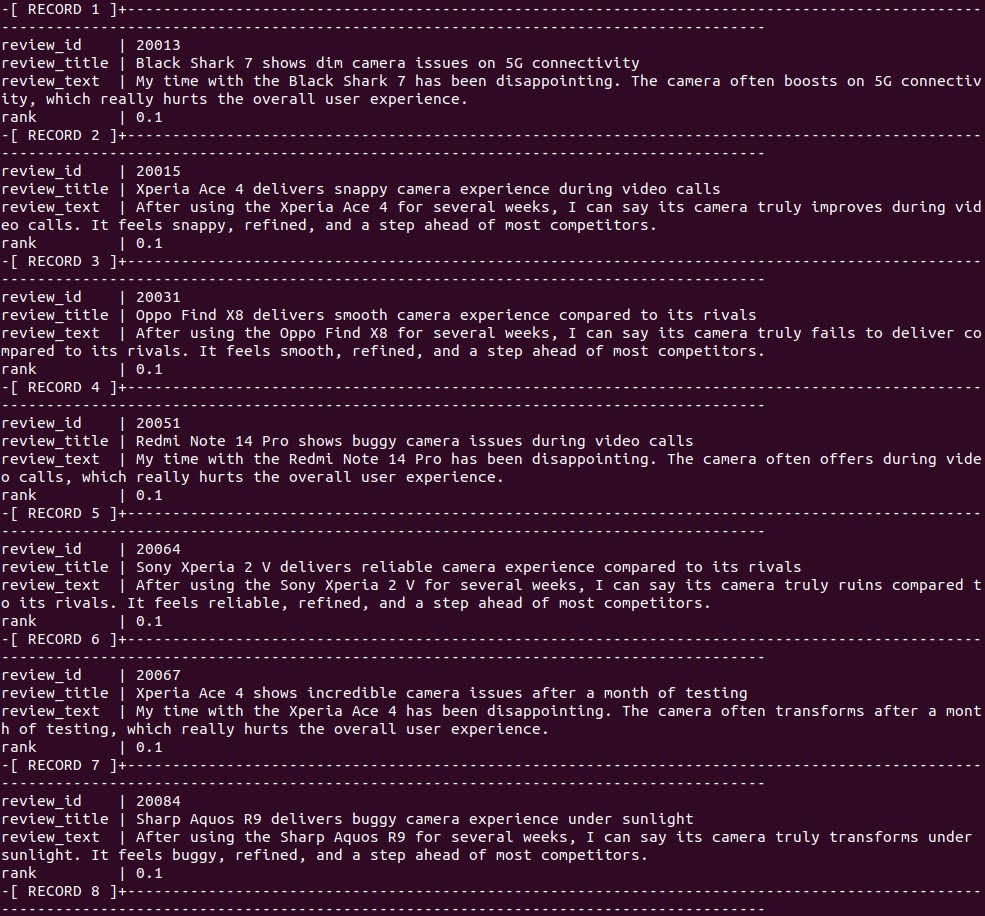
Each method has its strengths: full-text finds exact keyword matches, while vector search finds semantically similar results even without exact phrasing.
- Performing hybrid search
To combine results, use a two-part query: one subquery performs vector search, the other full-text. Then aggregate and re-rank using Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION rrf_score(rank int, rrf_k int DEFAULT 50) RETURNS numeric LANGUAGE SQL IMMUTABLE PARALLEL SAFE AS $$ SELECT COALESCE(1.0 / ($1 + $2), 0.0); $$; |
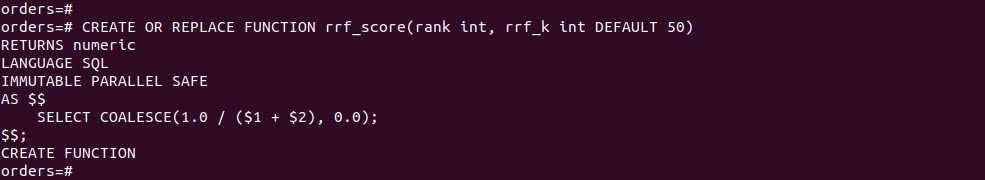
The hybrid query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
WITH q AS ( -- Query vector: select any embedding as the example vector SELECT embedding AS v FROM order_reviews ORDER BY review_id LIMIT 1 ), v_branch AS ( -- Vector similarity branch (embedding-based ranking) SELECT r.review_id, r.review_title, r.review_text, rank() OVER (ORDER BY r.embedding <-> q.v) AS r FROM order_reviews r, q ORDER BY r.embedding <-> q.v LIMIT 40 ), t_branch AS ( -- Text search branch (full-text search ranking) SELECT review_id, review_title, review_text, rank() OVER ( ORDER BY ts_rank_cd( to_tsvector('english', review_text), plainto_tsquery('english', 'camera') ) DESC ) AS r FROM order_reviews WHERE to_tsvector('english', review_text) @@ plainto_tsquery('english', 'camera') ORDER BY ts_rank_cd( to_tsvector('english', review_text), plainto_tsquery('english', 'camera') ) DESC LIMIT 40 ), searches AS ( SELECT * FROM v_branch UNION ALL SELECT * FROM t_branch ) SELECT review_id, review_title, review_text, SUM(rrf_score(r::int)) AS score FROM searches GROUP BY review_id, review_title, review_text ORDER BY score DESC LIMIT 10; |
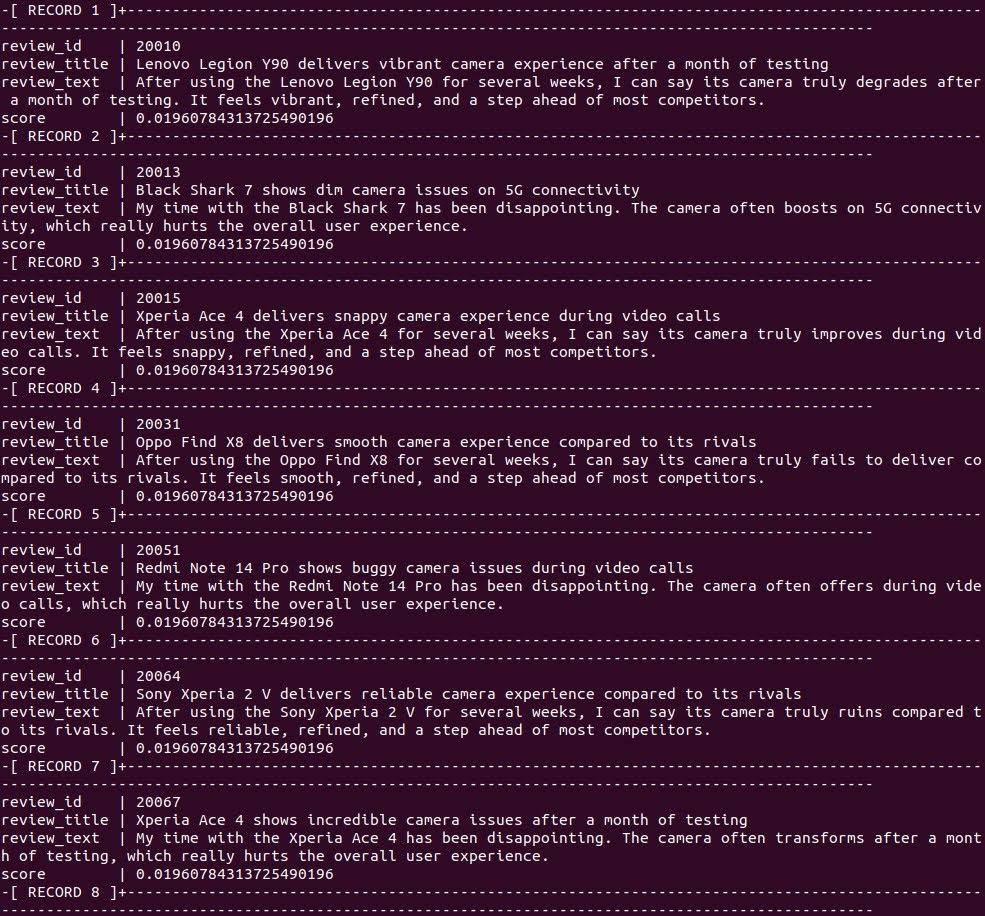
This returns the top 10 results ranked by a fusion of their full-text and vector ranks.
- Performance insights
While this example uses a small, randomly generated dataset, execution plans show both indexes are used efficiently. The hybrid approach boosts results that rank well in both dimensions, improving recall and relevance without external tools.
Revolutionize Data Handling with Instaclustr for PostgreSQL and pgvector
Instaclustr for PostgreSQL is revolutionizing how applications handle complex data by integrating the powerful pgvector extension. This enhancement unlocks advanced hybrid search capabilities, combining traditional filtered searches with sophisticated vector similarity searches. This synergy allows developers to build smarter, more intuitive applications, such as powerful recommendation engines, AI-driven analytics platforms, and semantic search tools that understand user intent, not just keywords. By storing and querying vector embeddings directly within the familiar PostgreSQL environment, users can perform nearest neighbor searches with exceptional speed and precision, finding the most relevant data points in vast datasets.
The real power of pgvector lies in its seamless integration with PostgreSQL’s robust, battle-tested architecture. This provides cutting-edge performance of vector search and the reliability of a leading open source relational database. By combining vector similarity search with standard SQL filters, users can create highly refined queries that deliver more accurate and context-aware results. For example, search for products that are not only semantically similar but also meet specific criteria like price range, brand, or availability, all within a single, efficient query. This hybrid approach significantly improves the user experience and opens up new possibilities for data interaction.
With Instaclustr, leveraging pgvector in PostgreSQL is straightforward and secure. Instaclustr manages the complexities of deployment, optimization, and maintenance, allowing teams to focus on building innovative features. The Instaclustr Managed Platform ensures PostgreSQL clusters are reliable, scalable, and secure, providing the solid foundation needed for demanding AI and search workloads. Instaclustr handles the heavy lifting of cluster management, from automated backups and monitoring to expert technical support, so users can confidently scale applications and unlock the full potential of pgvector’s hybrid search capabilities without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
For more information: