What Is a managed open source database?
Managed open source databases are cloud-based database services that leverage open source database software, but the service provider handles the infrastructure management, maintenance, and scaling. This allows users to benefit from open source flexibility and cost-effectiveness without the operational overhead of managing the database themselves.
Service providers for managed open source databases oversee routine operations such as patching, scaling, backup, monitoring, and security compliance. This provides value, but also comes at a cost: running open source databases as a managed service typically incurs ongoing costs related to the level of services provided, the computing resources used, and the volume of data storage required.
This is part of a series of articles about open source AI
Key benefits of managed open source databases
Managed open source databases offer a simplified path to using database technologies without the operational burden. By outsourcing management tasks to experienced providers, organizations can unlock several technical and business advantages:
- Reduced operational overhead: Routine tasks like provisioning, configuration, patching, monitoring, and backups are automated or handled by the provider. This reduces the need for dedicated database administrators and lowers the risk of human error.
- Cost-effectiveness: Leveraging open source software eliminates licensing fees, and managed services reduce the need for in-house infrastructure and expertise. This leads to predictable, usage-based pricing that aligns with organizational budgets.
- Scalability and performance: Managed platforms typically offer built-in scaling mechanisms, both vertical and horizontal. Resources can be adjusted dynamically based on workload, ensuring consistent performance under varying demand.
- Focus on application development: Developers can concentrate on building and optimizing applications without being distracted by database maintenance. This accelerates development cycles and improves time to market.
- Access to expert support: Managed service providers usually offer 24/7 support with experienced engineers. This ensures faster issue resolution and guidance on best practices for database performance, security, and reliability.
Key features of managed open source databases tools
Automated provisioning and deployment
Automated provisioning and deployment enable organizations to quickly spin up new database instances with standardized configurations and best practices pre-applied. This removes the need for manual setup and reduces the time required to make databases operational. Cloud-native APIs or management consoles make the process largely self-service and repeatable, ensuring consistency across environments.
Automation in deployment extends to consistent updates and repeating environments for testing, staging, and production. The managed approach lowers the probability of configuration drift and misconfiguration. It allows organizations to maintain database environments in sync and respond promptly to changing application needs.
Automatic backups and recovery
Managed open source databases offer fully automated backup schedules, often with versioning and retention policies that are configurable through simple dashboards or APIs. This ensures that critical business data is routinely protected without relying on manual intervention or periodic checks. Providers typically store backups in multiple physical locations or regions, adding another level of resilience against data loss.
Recovery workflows are also simplified and able to restore databases from any backup with minimal downtime. In disaster or data corruption scenarios, these features enable rapid recovery to a specific point in time, ensuring business continuity. Users also benefit from granular restore options, such as single-table or row-level recovery.
High availability and failover
High availability in managed open source databases is achieved by replicating data across multiple nodes or availability zones. This design ensures that if one node or even an entire region fails, the database remains online and accessible, shifting workloads automatically. Providers typically implement automatic failover mechanisms, switching connections from a failed primary node to a standby replica with no or minimal interruption to ongoing transactions.
These capabilities are crucial for mission-critical applications where downtime equates to direct business losses. Managed platforms often offer customizable replication strategies and service-level agreements (SLAs) for availability. The built-in failover mechanisms mean enterprises can meet business continuity objectives without building custom architectures.
Monitoring and performance insights
Managed open source database services usually provide deep visibility into database performance metrics via dashboards, alerts, and APIs. This includes real-time and historical insights on throughput, latency, query execution, resource utilization, and abnormal patterns. Such transparency helps organizations detect bottlenecks and resolve performance issues before they escalate.
Monitoring tools come with pre-configured alert thresholds and integration options for external observability platforms. Features like query analysis, slow-query logging, and index recommendations are built in, guiding database optimization efforts. Engineering teams can make data-driven decisions, tune workloads, and maintain optimal application performance.
Learn more in our detailed guide to open source monitoring
Security and compliance support
Security features in managed open source database platforms include encryption at rest and in transit, access controls, role-based permissions, and audit logging. Providers implement regular patching and updates to address known vulnerabilities, making it easier for organizations to keep data protected and meet security best practices by default.
Compliance management—covering standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS—is often integrated into the managed service. Features like isolated environments, audit trails, and pre-built compliance templates help organizations satisfy regulatory requirements with less manual work. Centralized security management also simplifies credential rotation, multi-factor authentication, and incident response, reducing the risk of breaches.
Notable managed open source databases solutions
1. NetApp Instaclustr

Instaclustr is a leading platform for open source database management, offering fully managed solutions that simplify the deployment, operation, and scaling of powerful open source technologies. Designed for businesses seeking reliability, performance, and scalability, Instaclustr provides a seamless way to manage databases without the complexity of manual configurations or maintenance.
By leveraging its expertise in open source technologies like Apache Cassandra, PostgreSQL, Kafka and OpenSearch, Instaclustr ensures high availability, robust security, and optimal performance for mission-critical applications. With a focus on automation, monitoring, and support, Instaclustr empowers organizations to focus on innovation while leaving the heavy lifting of database management to the experts.
Key features of Instaclustr
- Fully managed open source: Instaclustr provides end-to-end management of open source technologies like Apache Cassandra, PostgreSQL, Kafka, OpenSearch, and more, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
- High availability and scalability: The platform is designed to handle mission-critical workloads with ease, offering automatic failover, replication, and the ability to scale horizontally or vertically as needed.
- Comprehensive monitoring and alerts: Instaclustr includes advanced monitoring tools that provide real-time insights into database performance, with proactive alerts to address potential issues before they impact operations.
- Robust security: With features like encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control, and regular security updates, Instaclustr ensures that your data is protected at all times.
- 24/7 expert support: Instaclustr’s team of open source experts is available around the clock to provide assistance, troubleshoot issues, and ensure smooth database operations.
- Automated backups and disaster recovery: The platform offers automated backup solutions and disaster recovery options to safeguard data and minimize downtime in case of unexpected events.
- Multi-cloud and on-premise support: Instaclustr supports deployment across major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, as well as on-premise environments, offering flexibility to meet diverse infrastructure needs.
- Open source expertise: As a champion of open source technologies, Instaclustr ensures that its solutions are free from vendor lock-in, giving businesses the freedom to innovate and adapt.
- Achieve optimal outcomes for GenAI projects: Leverage existing technologies such as Cassandra, PostgreSQL or OpenSearch to enhance AI outcomes with vector search capabilities and move GenAI projects from pilot to production.
2. Amazon RDS

Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) is a managed relational database solution to simplify and automate database operations such as provisioning, configuration, patching, and backups. It supports multiple open source engines including PostgreSQL and MySQL, allowing users to launch fully managed databases.
Key features include:
- Support for multiple engines: Deploys open source engines like MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as proprietary ones like SQL Server and Oracle.
- Automated management: Handles provisioning, backups, patching, and recovery to minimize administrative overhead.
- High availability: Offers Multi-AZ deployments with automatic failover and synchronous replication.
- Performance optimization: Includes features such as optimized reads/writes, two readable standbys, and support for AWS Graviton3-based instances.
- Scalability: Scales compute and storage independently to match workload requirements.

Source: Amazon
3. Azure Database for MySQL and PostgreSQL

Azure Database for MySQL and Azure Database for PostgreSQL are fully managed, cloud-based implementations of their respective open source engines. These services eliminate the overhead of managing infrastructure, backups, updates, and scaling, while providing high availability and enterprise-grade security.
Key features of Azure Database for MySQL include:
- Open source compatibility: Fully managed MySQL, based on the latest community edition, ensures seamless migration and operational flexibility.
- Performance insights: Provides performance tuning recommendations to help optimize query execution and resource usage.
- Security: Includes Microsoft Defender integration for threat detection, advanced security controls, and compliance support.
- Azure ecosystem integration: Works natively with Azure App Service, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and other Azure tools.
- Cost optimization: Helps reduce total cost of ownership by eliminating licensing fees and operational overhead, with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Key features of Azure Database for PostgreSQL include:
- AI capabilities: Leverages native vector search, local embeddings, and Azure AI extensions to support generative AI and machine learning workloads.
- Autonomous tuning: Uses machine learning algorithms to automatically tune performance and reduce manual optimization efforts.
- Distributed PostgreSQL support: Offers elastic clusters to scale PostgreSQL across nodes.
- Extension support: Includes PostGIS, PLV8, JSONB, geospatial tools, and popular language bindings like Python, Ruby, and Java.
- Scalability and availability: Supports automated maintenance, patching, and near-zero downtime scaling for compute and storage.

Source: Microsoft
4. MongoDB Atlas

MongoDB Atlas is a managed cloud database service to simplify the deployment and scaling of MongoDB applications. Built around the document model, Atlas enables developers to work with data in a way that naturally aligns with application design. It abstracts away infrastructure and operational concerns such as backups, patching, scaling, and availability.
Key features include:
- Flexible document model: Uses JSON-like documents to store and query data, enabling rapid development and easier schema evolution.
- AI integration and vector search: Built-in support for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and vector search allows developers to build AI-powered applications that are scalable and responsive.
- Global scalability: Supports multi-region and multi-cloud deployments across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, with workload isolation and automated failover.
- Performance optimization: Automatically adjusts resources based on workload, optimizes queries through built-in tools, and performs upgrades to ensure speed and reliability.
- Search and analytics: Includes native support for full-text search, vector search, and real-time analytics, enabling querying and data processing without external tools.
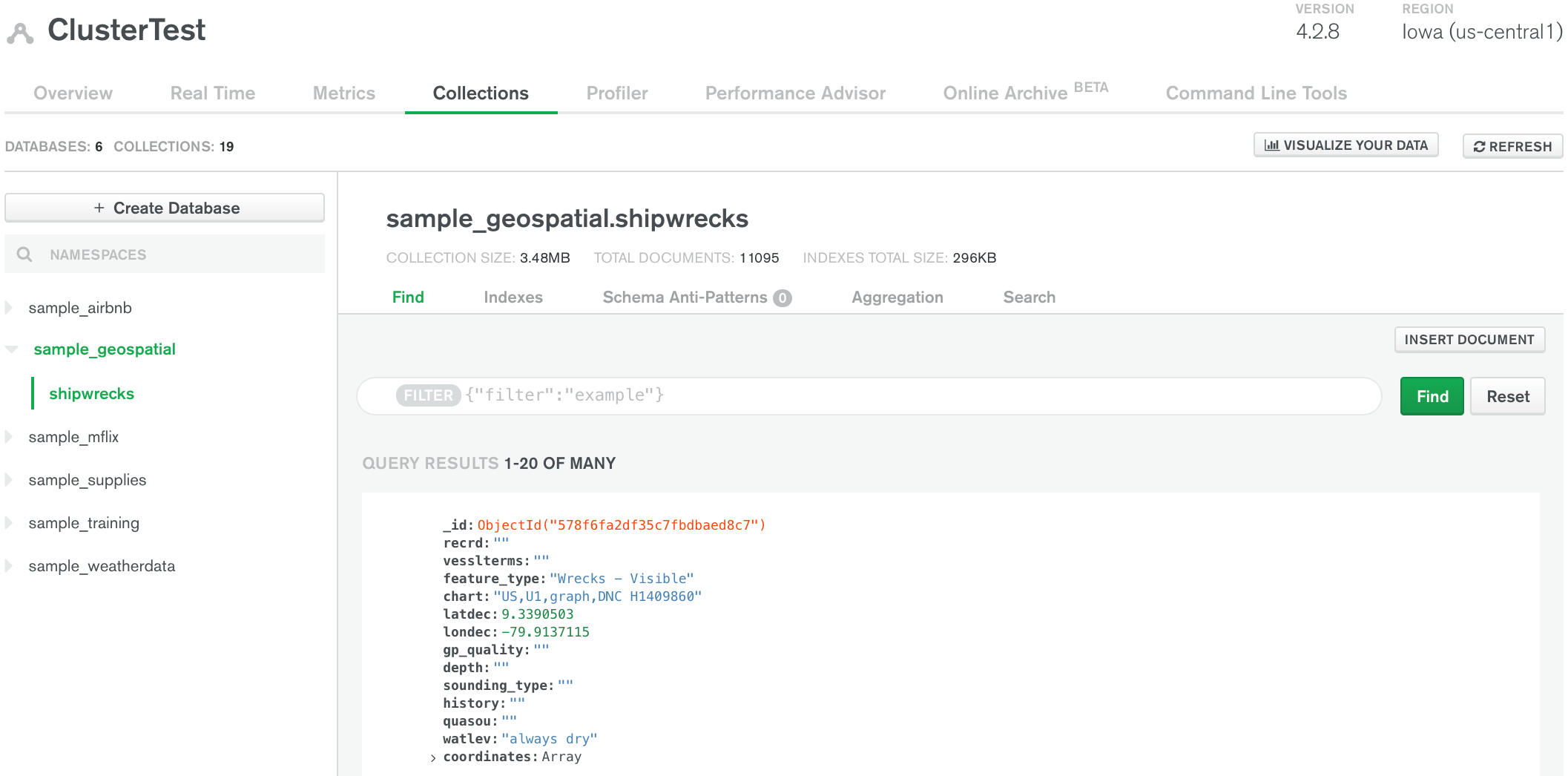
Source: MongoDB
5. Dragonfly Cloud

Dragonfly Cloud is a fully managed, high-performance in-memory data store designed as a drop-in replacement for Redis and Memcached. It delivers higher throughput and lower latency while reducing infrastructure costs. Users can choose their cloud provider, region, and memory allocation, while the service manages scaling, performance tuning, and reliability.
Key features include:
- High performance: Processes workloads up to 25× faster than Redis.
- Cost efficiency: Reduces infrastructure expenses by up to 80% through optimized hardware utilization.
- Scaling: Scales automatically based on memory capacity to handle unpredictable traffic spikes.
- Full compatibility: Works with Redis and Memcached APIs without requiring code changes.
- Flexible deployment: Runs on the cloud and region of your choice for low-latency integration.
6. CockroachDB Cloud

CockroachDB Cloud is a managed distributed SQL database service to simplify operations while delivering resilience, scalability, and transactional consistency. It removes the complexities of traditional database management with automated provisioning, scaling, backups, and updates.
Key features include:
- Managed operations: Automates provisioning, scaling, patching, and backups.
- Horizontal scaling: Automatically scales reads and writes across nodes without manual sharding.
- High availability: Offers up to 99.999% availability with multi-active clusters and rolling upgrades.
- ACID transactions at scale: Maintains transactional integrity across distributed environments, even under high concurrency and workload pressure.
- Global low-latency: Spans data across regions to keep it close to users, reducing latency.
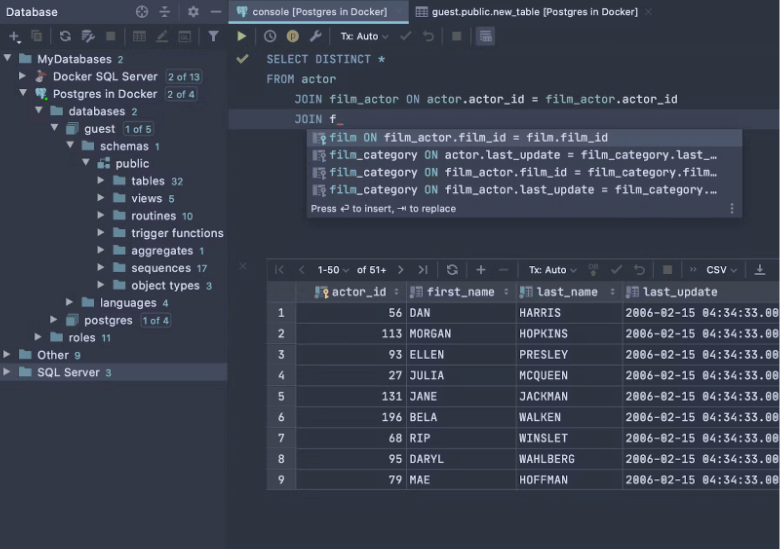
Source: CockroachDB
Conclusion
Managed open source databases offer a compelling combination of open source flexibility and enterprise-grade operational support. They abstract the complexity of database administration while delivering automation, scalability, and integrated security. This allows organizations to deploy reliable, performant data infrastructure without diverting resources from core development efforts.