What Are Agentic AI Frameworks?
Agentic AI frameworks are software toolkits that simplify the creation of autonomous AI agents, providing developers with pre-built components for tasks like perception, reasoning, action, and memory management to build complex, goal-driven systems.
Popular frameworks include CrewAI, LangGraph, AutoGen, LlamaIndex, AutoAgent, DSPy, Haystack, and Microsoft Semantic Kernel, which offer varying capabilities for single-agent and multi-agent orchestration, tool integration, and data retrieval. These frameworks simplify AI development by abstracting complexity, enabling rapid prototyping, and scaling from simple to sophisticated autonomous applications.
Agentic frameworks act as blueprints and toolkits for constructing AI agents; systems designed to perceive, reason, and act to achieve specific goals autonomously. They provide developers with the necessary building blocks to create intelligent agents that can interact with external systems, make decisions, and manage context over time.
In this article:
- Benefits of Agentic AI Frameworks
- Notable Agentic AI Frameworks
- How to Choose the Right Agentic AI Framework
Benefits of Agentic AI Frameworks
Agentic AI frameworks offer a range of advantages for building intelligent, autonomous systems that can operate in complex environments. Their structured approach to agent design and task execution enables more flexible and maintainable AI applications.
- Task decomposition and autonomy: Agents can break down complex goals into smaller tasks, make decisions independently, and execute actions without constant human input.
- Built-in memory and context handling: Persistent memory lets agents retain relevant information across sessions, improving coherence, personalization, and long-term task performance.
- Multi-agent coordination: Frameworks support communication and collaboration among multiple agents, enabling parallel task execution and specialization.
- Tool and API integration: Agents can be connected to external tools, APIs, and databases, allowing them to interact with real-world systems and perform actions beyond language generation.
- Modularity and reusability: Agent behaviors, tools, and memory modules are often designed as reusable components, accelerating development and simplifying maintenance.
- Support for iteration and self-correction: Agents can evaluate outcomes, revise plans, and retry failed steps, making them more resilient in dynamic or uncertain environments.
- Scalable architecture: Many frameworks provide infrastructure for managing large agent systems, supporting use cases from personal assistants to enterprise-level automation.
The Importance of Scalable, Efficient, and Reliable Data Infrastructure
Agentic AI frameworks are only as powerful as the data infrastructure supporting them. While the agents themselves provide the reasoning and autonomy, they rely heavily on a continuous flow of high-quality data to perceive their environment, learn from context, and execute decisions. Without a robust backend, even the most sophisticated agents can face bottlenecks, memory loss, or latency issues that cripple their performance.
This is where proven open source technologies become the unsung heroes of AI development. Tools like Apache Kafka®, Apache Cassandra®, PostgreSQL®, OpenSearch®, and ClickHouse® provide the critical foundation needed for scalable, efficient, and reliable agentic operations.
Enabling real-time data ingestion and processing
Autonomous agents often operate in dynamic environments where seconds matter. Whether it’s a customer service bot handling thousands of concurrent requests or a supply chain agent reacting to shipping delays, real-time data ingestion is non-negotiable.
Apache Kafka serves as the central nervous system for these high-velocity data streams. It allows agents to subscribe to real-time events, ensuring they always have the most current information to act upon. By decoupling data producers from consumers, Kafka ensures that agents can process streams of information—like sensor data or user interactions—without overwhelming the system, maintaining high throughput even during peak loads.
Managing complex state and memory
For an agent to be truly “agentic,” it must remember past interactions and maintain context over long periods. This requires persistent storage that is both fast and reliable.
Apache Cassandra and PostgreSQL are essential for managing this stateful information. Cassandra’s distributed architecture makes it ideal for handling massive write workloads across multiple regions, ensuring agents have high availability access to their operational history. Meanwhile, PostgreSQL offers robust relational data integrity, perfect for handling structured transactional data that agents may need to query or update as part of their decision-making workflow.
Powering retrieval and analytics
Agents don’t just react; they research. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a core component of many frameworks, allowing agents to pull relevant knowledge from vast datasets to inform their answers.
OpenSearch plays a pivotal role here by enabling fast, scalable vector search. It allows agents to perform semantic searches across unstructured data—like documents, logs, or chat history—to find the specific context they need to ground their responses in reality.
Similarly, ClickHouse empowers agents with analytical capabilities. Its column-oriented structure allows for lightning-fast analytical queries on large volumes of data. This enables agents to perform complex data analysis tasks on the fly, such as spotting trends or generating reports, adding a layer of analytical intelligence to their autonomous actions.
By leveraging these open source technologies developers can build Agentic AI systems that are not just smart, but enterprise-ready—capable of scaling effortlessly and operating reliably in the real world.
Related content: Learn how to power AI workloads with open source
Notable Agentic AI Frameworks
1. LangGraph
![]()
LangGraph is a flexible agentic AI framework that helps developers build controllable and customizable agent workflows. It emphasizes fine-grained control over agent behavior, making it suitable for applications where stability and transparency are crucial. LangGraph supports both human-in-the-loop moderation and persistent memory.
Key features include:
- Human-in-the-loop moderation: Add checks at critical points in the agent’s workflow to approve or steer decisions, improving reliability and alignment.
- Custom agent workflows: Use low-level primitives to define diverse control flows, such as single-agent loops, hierarchical task execution, or multi-agent collaboration.
- Persistent memory: Store and retrieve conversation history and task context across sessions to support long-term, coherent interactions.
- Real-time streaming: Provide immediate feedback by streaming tokens and agent reasoning steps as they happen, enhancing transparency and user experience.
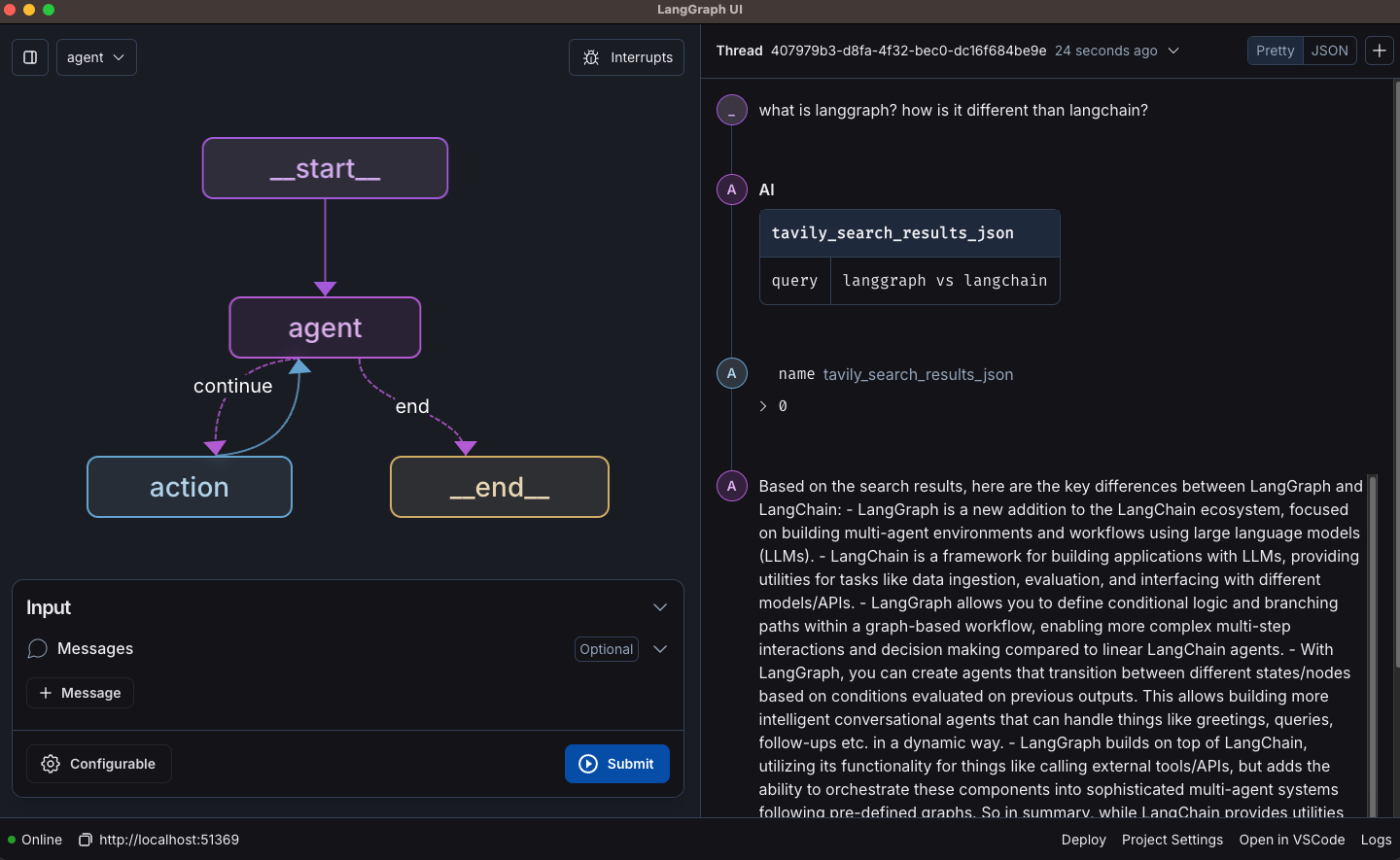
Source: LangChain
2. AutoGen

AutoGen is a modular framework for building single and multi-agent AI systems, offering tools for both non-coders and developers. It provides layered abstractions, from simple UI prototyping to multi-agent orchestration, making it adaptable for a range of use cases, from quick demos to production-ready workflows.
Key features include:
- No-code prototyping with Studio: A web-based UI for building agent workflows visually, suitable for beginners or rapid experimentation without writing code.
- Conversational agent framework with AgentChat: A Python-based API for designing and managing interactive single or multi-agent applications. Supports asynchronous execution and integration with models like gpt-4.
- Scalable orchestration with Core: An event-driven framework for creating complex, dynamic workflows across distributed agents. Suited for business automation, research, and multi-language systems.
Integration via extensions: A set of adapters and plugins that connect agents to external services, such as the OpenAI Assistant API, Docker-based code execution, or custom gRPC runtimes. Enables real-world applications by bridging agents with infrastructure and tools.
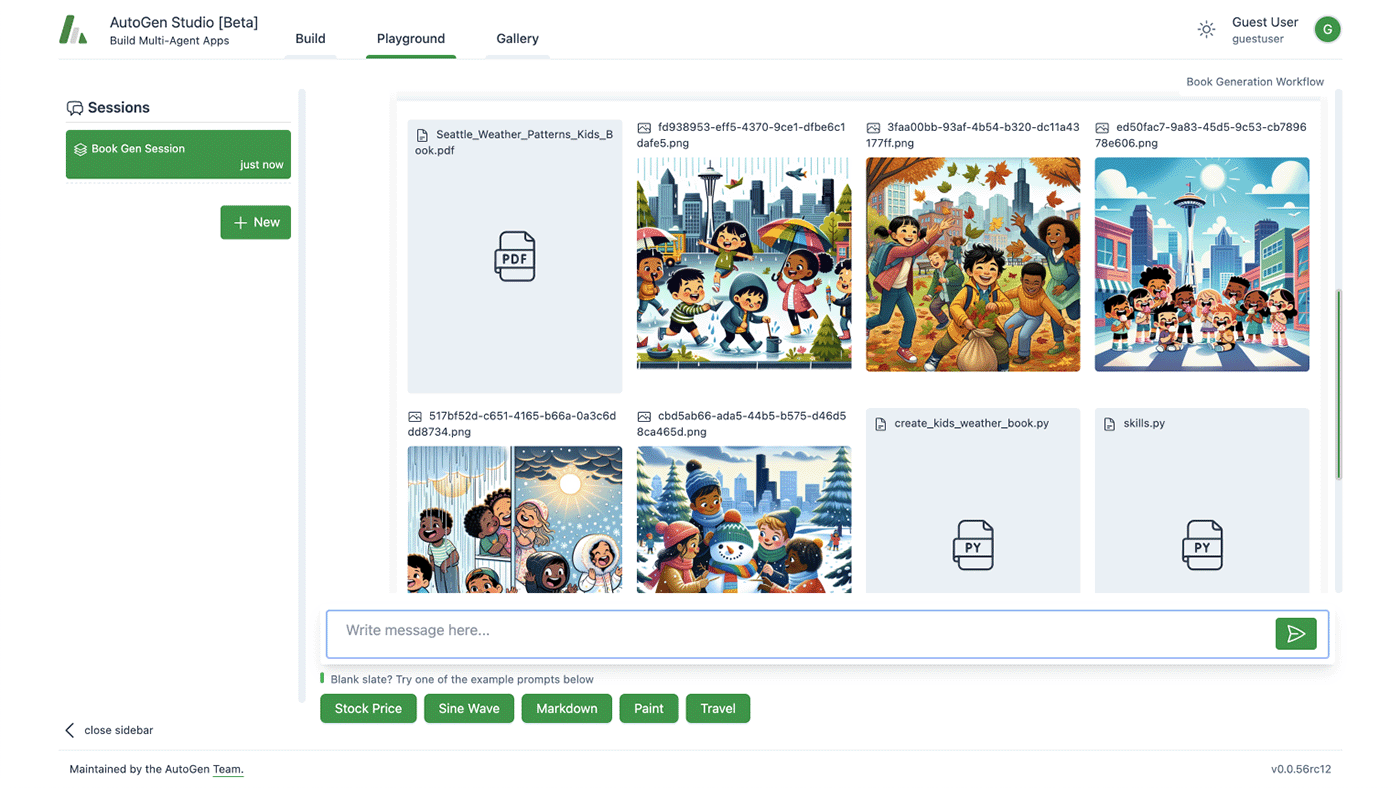
Source: AutoGen
3. CrewAI

CrewAI is an open-source framework to simplify the creation and coordination of high-performing multi-agent systems. It enables developers to define, manage, and deploy autonomous agents that can collaborate to complete complex workflows.
Key features include:
- Role-based agent design: Developers can define agents with roles, goals, and behaviors, allowing for specialization and more effective collaboration within the crew.
- Task assignment engine: Tasks can be explicitly defined and assigned to individual agents, promoting structured execution and clarity in multi-agent workflows.
- One-command execution: After configuration, crews can be launched with a single command, enabling quick deployment and monitoring of agent activity.
- Scalable multi-agent support: Proven to handle millions of agents monthly, CrewAI is built to operate at scale while maintaining performance and reliability.
- Human-readable configuration: The framework emphasizes developer experience by making it easy to set up agents and tasks through declarative configurations.
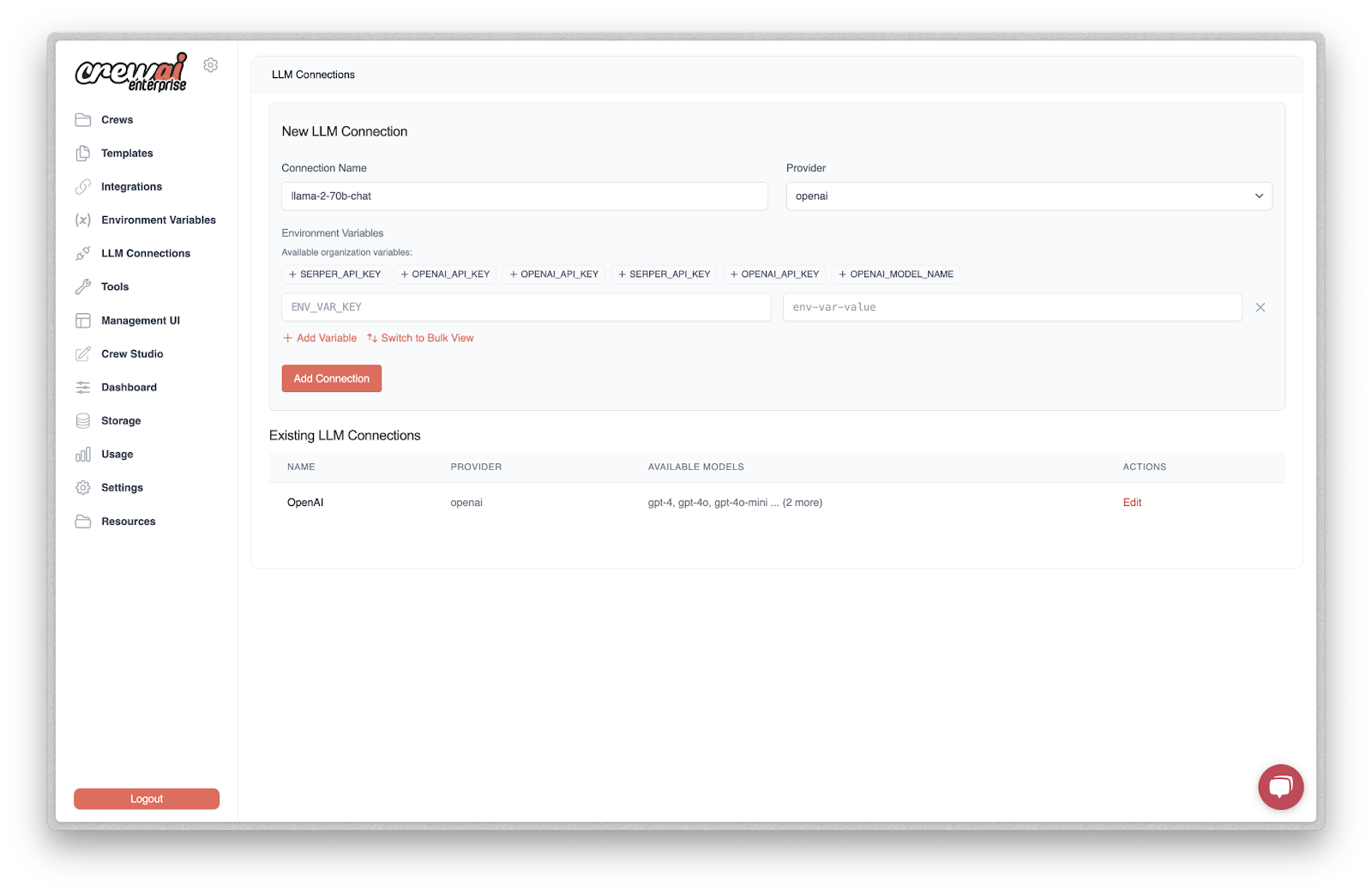
Source: CrewAI
4. LlamaIndex

LlamaIndex is a framework for building agentic AI workflows that extract, synthesize, and act on complex document-based knowledge. It enables developers to create context-augmented agents capable of handling real-world enterprise data, from financial reports to scanned PDFs. It includes tools for document ingestion, parsing, indexing, and retrieval.
Key features include:
- Context-augmented agent framework: Build agents that can reason over enterprise documents by combining language models with structured retrieval pipelines and context-aware memory.
- Document parsing: The LlamaParse engine extracts information from tables, charts, images, nested headers, and handwritten notes across over 300 document formats.
- LlamaCloud infrastructure: A hosted platform that automates data ingestion and context management, enabling teams to focus on building applications instead of maintaining pipelines.
- Production-ready RAG pipelines: Modular architecture lets developers customize retrieval and orchestration logic to suit business needs while ensuring performance and scalability.
- Enterprise-grade scalability: Designed to handle millions of documents with persistent data connectors and high-throughput processing.
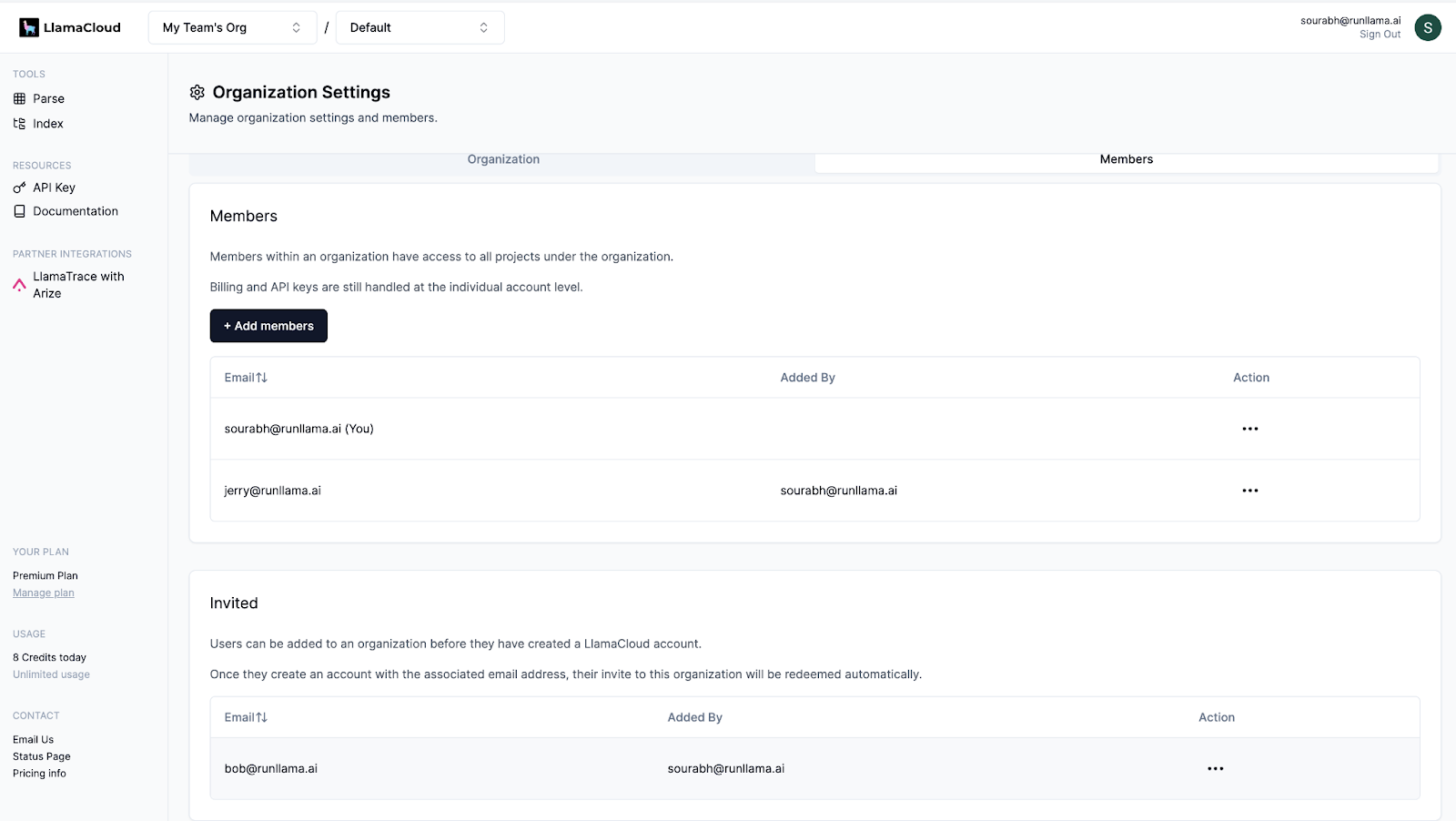
Source: LlamaIndex
5. Semantic Kernel

Semantic Kernel is an open-source SDK to help developers build AI agents and integrate modern language models into C#, Python, or Java applications. Acting as a lightweight middleware layer, it connects AI capabilities with enterprise systems, enabling automation, orchestration, and multi-modal interaction.
Key features include:
- Multi-language support: Fully supported in C#, Python, and Java with version 1.0+, offering consistent APIs and long-term stability across platforms.
- Middleware for model-to-function execution: Translates model-generated requests into function calls using existing code, enabling automation of business logic without complex rewrites.
- Modular plugin architecture: Integrate services as plugins using OpenAPI specs. Connect external systems like Microsoft 365 Copilot or internal APIs for broader functionality.
- Enterprise-ready observability and security: Built-in telemetry, hooks, and filters help monitor and govern AI behavior at scale, supporting secure and compliant deployments.
- Future-proof model integration: Swap in new AI models without re-architecting the application, allowing the system to evolve as the model ecosystem advances.
Source: Microsoft
6. AutoAgent

AutoAgent is a fully automated, zero-code framework for building and deploying LLM agents using natural language. It removes the complexity of traditional agent frameworks by allowing users to create agents, tools, and workflows conversationally, without writing code.
Key features include:
- Zero-code agent creation: Build agents, tools, and workflows entirely through natural language using the agent or workflow editor. No programming required.
- Out-of-the-box multi-agent system: The built-in “User Mode” provides a ready-to-use AI assistant comparable to OpenAI’s Deep Research, but open-source and cost-effective.
- Self-managing vector database: Built-in vector storage supports agentic RAG pipelines with automated context management, outperforming traditional solutions like LangChain.
- LLM compatibility: Integrates with a range of language models, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Deepseek, Hugging Face, Grok, and Gemini.
- Flexible interaction modes: Supports both function-calling and ReAct paradigms for agent reasoning and decision-making.
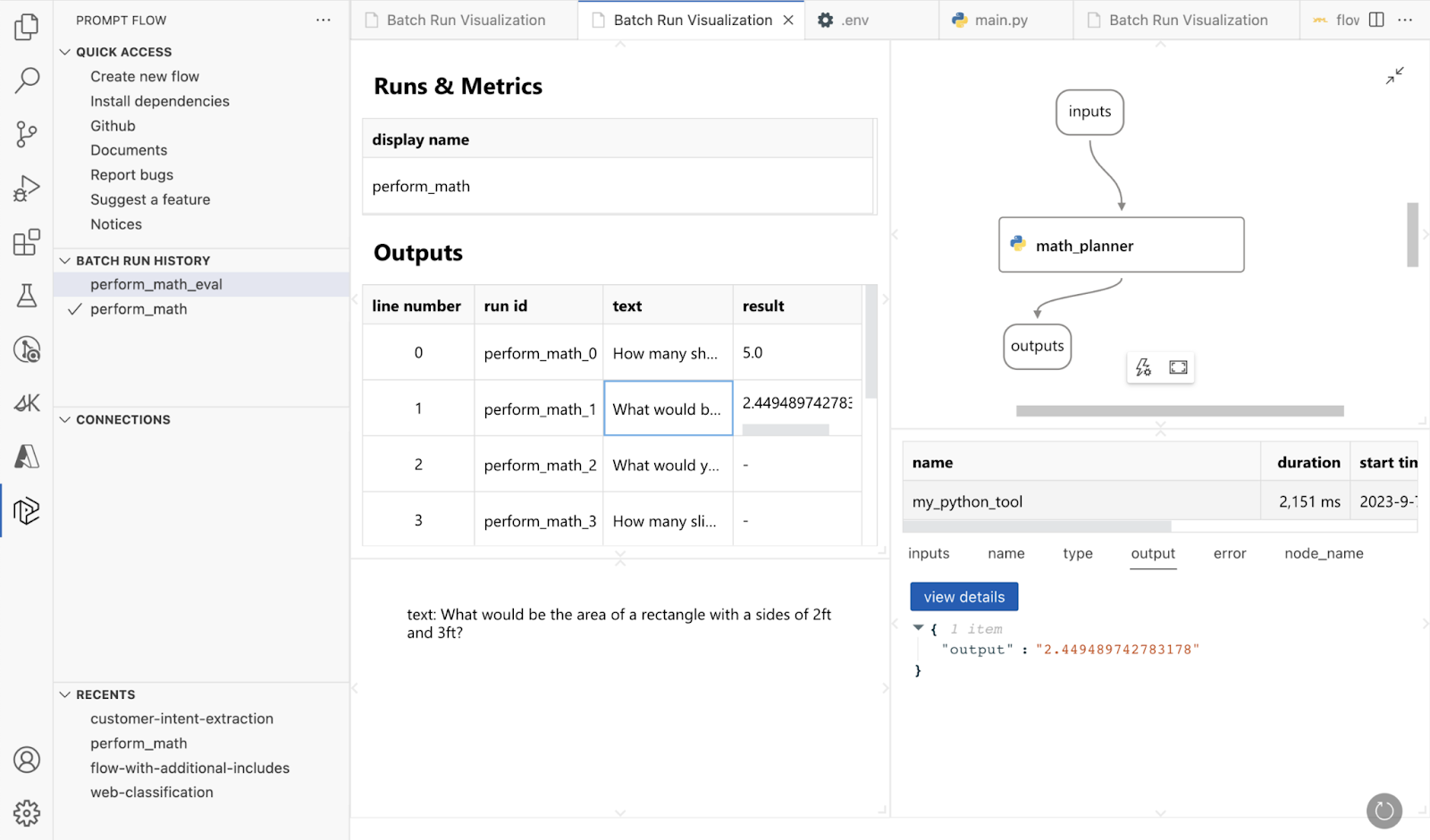
7. DSPy

DSPy (declarative self-improving Python) is a high-level framework for building modular AI systems using declarative programming. Instead of manually crafting prompts or fine-tuning models for every use case, DSPy lets users define AI behavior through structured modules.
Key features include:
- Declarative AI programming: Define AI components using typed input/output signatures. Modules like dspy.Predict, dspy.ChainOfThought, or dspy.ReAct translate these into optimized prompts and structured outputs.
- Model-agnostic integration: Easily switch between LLMs (OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Databricks, local models) without changing system logic. DSPy abstracts model-specific quirks to keep code stable and reusable.
- Optimizers for prompt & weight tuning: Built-in optimizers (e.g. MIPROv2, BootstrapRS, BootstrapFinetune) automatically generate examples or tune prompts/weights to improve performance on real datasets.
- Support for complex pipelines: Build multi-stage AI pipelines like agent loops, retrieval-augmented generation, or reasoning tasks by composing multiple DSPy modules into a unified system.
- Rapid prototyping & iteration: Quickly experiment with different strategies and task setups by swapping modules or optimization objectives.
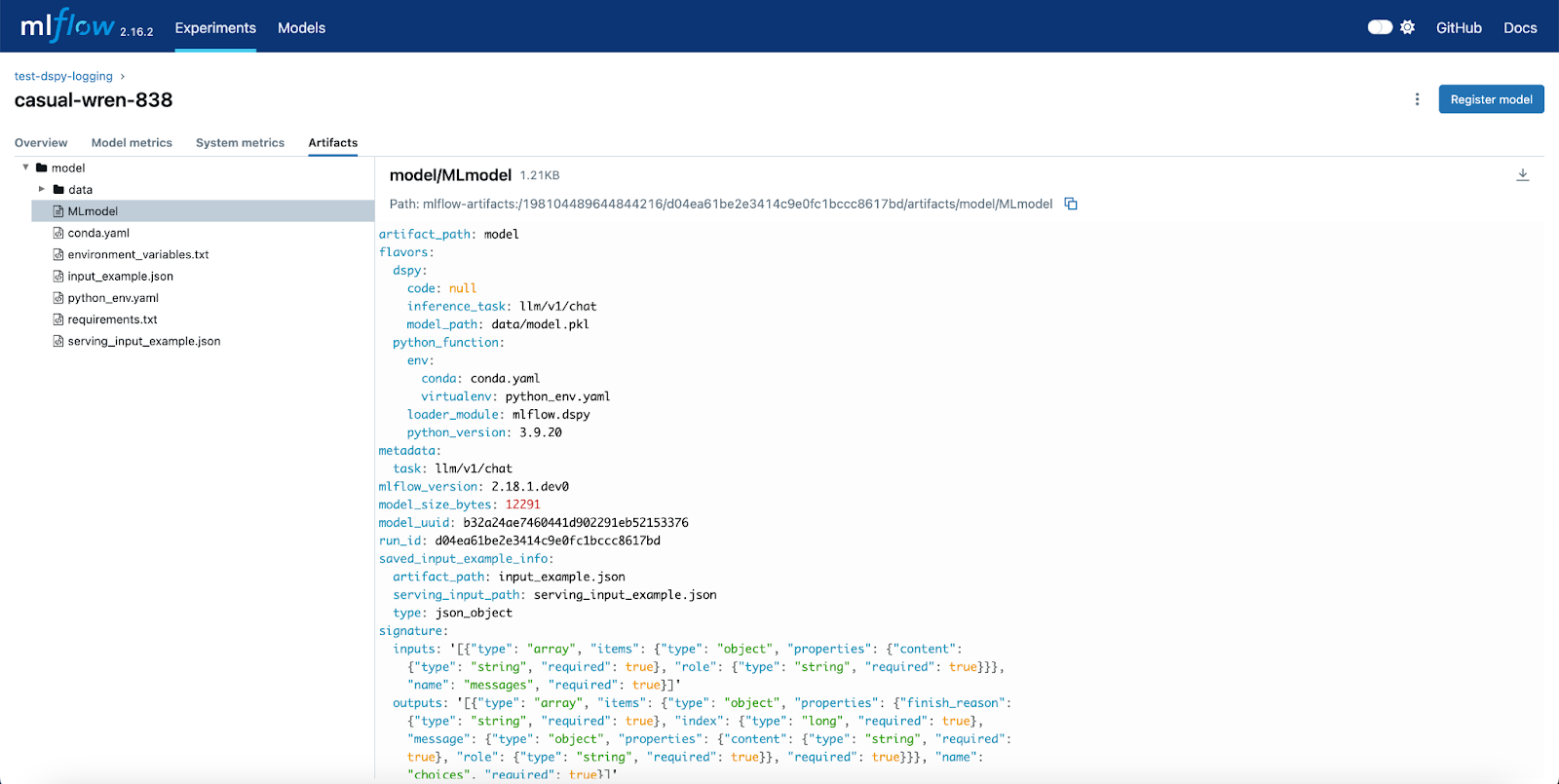
Source: DSPy
8. Haystack

Haystack is a production-ready, open-source framework for building AI applications using large language models and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). It lets developers construct modular pipelines that integrate with various LLMs, vector databases, and external tools.
Key features include:
- Flexible pipeline architecture: Design custom AI workflows using modular components. Pipelines are fully serializable and can handle everything from simple RAG systems to multi-agent orchestration.
- Multimodal AI support: Build apps that work across modalities like text, images, and audio. Haystack supports use cases like image generation, captioning, and transcription.
- Conversational AI interfaces: Use standardized chat interfaces to create production-ready conversational agents. Focus on UX while Haystack handles the backend logic.
- Content generation engines: Leverage prompt templates and flexible orchestration to build content generation pipelines tailored to business needs.
- Agentic pipelines: Combine LLMs with tools through function-calling interfaces. Build dynamic agent workflows with branching, looping, and complex decision logic.
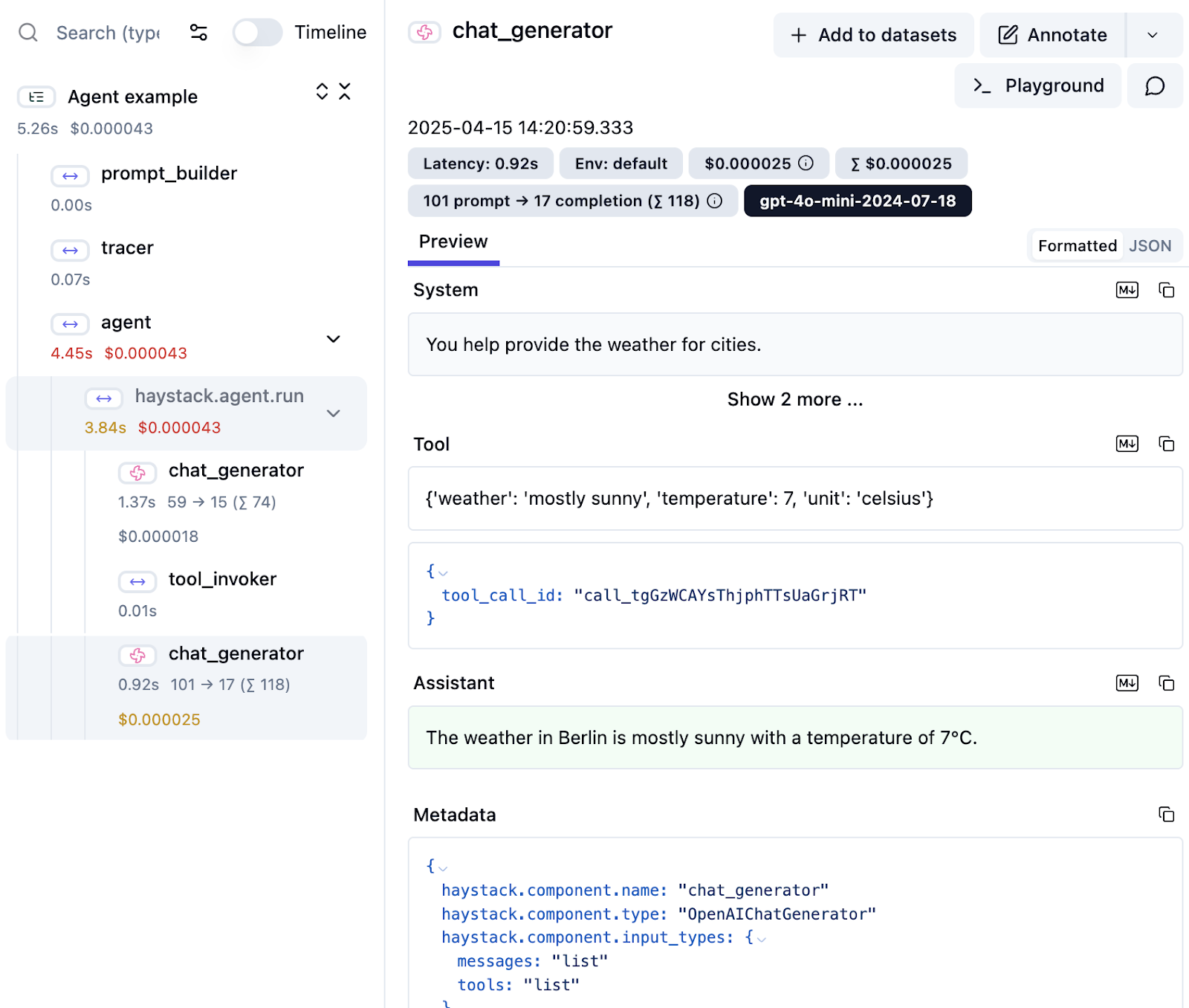
Source: Haystack
Related content: Read our guide to agentic AI tools (coming soon)
Tips from the expert

David vonThenen
Senior AI/ML Engineer
As an AI/ML engineer and developer advocate, David lives at the intersection of real-world engineering and developer empowerment. He thrives on translating advanced AI concepts into reliable, production-grade systems all while contributing to the open source community and inspiring peers at global tech conferences.
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better apply and optimize agentic AI frameworks for scalable, autonomous systems:
- Prototype agents using synthetic tasks before real integration: Before connecting agents to real APIs or sensitive data, design synthetic environments to simulate goals, failure modes, and tool usage. This helps refine planning logic and test agent robustness under controlled conditions.
- Design tool wrappers with explicit preconditions and postconditions: Tools exposed to agents should declare what they need (inputs) and guarantee (outputs). This prevents agents from misusing tools and improves interpretability, composability, and automated debugging of workflows.
- Build shared memory abstractions for multi-agent collaboration: Instead of duplicating memory modules per agent, create shared, versioned memory stores (e.g., vector + relational) with scoped access. This allows agents to reason jointly while maintaining separation of responsibilities.
- Use role archetypes to constrain agent behavior in multi-agent setups: Define role-based personas like “Planner,” “Researcher,” or “Reviewer,” each with limited tools, memory access, and goals. This minimizes errors, supports explainability, and aligns agents with human-readable workflows.
Log intermediate reasoning chains and decisions for traceability: Instrument all agent decisions (tool choice, thought steps, memory updates) with structured logs or metadata. This is essential for auditing, debugging, and training future self-improving agents via offline RL or fine-tuning.
How to Choose the Right Agentic AI Framework
Here are some of the factors that organizations should consider when choosing an agentic AI framework.
1. Assess Autonomy, Planning and Memory Features
When choosing an agentic AI framework, start by evaluating its support for autonomy, planning, and memory management. Some frameworks emphasize task decomposition, long-term memory, and self-correction, which enable agents to handle complex, multi-stage processes with minimal oversight. Assess whether the framework offers abstractions for persistent context, stateful interactions, and the ability for agents to reason over time, as these are crucial for most real-world applications.
Additionally, consider the flexibility of the planning mechanisms: can agents dynamically react to new information or environmental changes? Frameworks that support fine-grained control over memory, context, and planning logic ensure that AI agents remain effective and reliable as task complexity grows. Review documentation, inspect example architectures, and test out sample agents to validate these capabilities before making a commitment.
2. Performance Under Scale
Performance at scale is key when deploying agentic AI solutions in production. Some frameworks are optimized for prototyping but may falter under high concurrency, large user bases, or heavy data processing loads. Review performance benchmarks, parallelization strategies, and scalability features such as distributed orchestration or asynchronous execution. Good frameworks allow agents to operate efficiently even in demanding, real-world environments.
It’s also important to understand how a framework handles resource allocation and system bottlenecks. Scalable agentic frameworks should provide mechanisms for task prioritization, error handling under load, and monitoring resource utilization. Consider running scaled-up simulations or load tests with the target workload to reveal potential performance issues.
3. Support for Multi-Agent Coordination
Multi-agent coordination can dramatically increase agentic system effectiveness, allowing distributed problem-solving and division of labor. Evaluate whether a framework supports multiple agents working in parallel or collaborative arrangements. Look for features like role management, inter-agent communication protocols, and workflow orchestration for multi-agent tasks.
Frameworks designed for multi-agent scenarios often include mechanisms for conflict resolution, consensus-building, and shared memory architectures. These are essential for applications requiring agents to negotiate resources, jointly plan actions, or hand off tasks smoothly.
4. Security and Governance
Security and governance are paramount as agentic AI solutions interact with sensitive data and critical business systems. Assess whether a framework provides granular access control, audit logging, and policy enforcement tools. Effective governance features help ensure agents operate within defined ethical, compliance, and operational boundaries while protecting against misuse.
Consider also the framework’s support for monitoring, explainability, and traceability of agent actions. Strong governance tools are needed to track decision-making processes, investigate failures, and meet regulatory requirements.
5. Tool and API Integration
Finally, the ability to integrate with external tools, APIs, and data sources directly impacts the usefulness of an agentic AI framework. Check for support for standard connectors, plugin architectures, and customization points for integrating proprietary or third-party services. Frameworks with robust integration capabilities let agents leverage a broader set of tools for task completion, resulting in more capable, adaptable solutions.
Evaluate the simplicity of adding or updating tool integrations and the framework’s support for secure, well-documented APIs. Consider how agent workflows handle API errors, changes, or deprecations to ensure reliability in production environments.
Instaclustr and the Rise of Agentic AI Frameworks
Instaclustr, a trusted provider of fully managed open source data infrastructure, plays a pivotal role in enabling the seamless integration of agentic AI frameworks into modern business ecosystems. By offering managed services for technologies like Apache Cassandra, Apache Kafka, PostgreSQL, ClickHouse, OpenSearch and Cadence, Instaclustr provides the robust, scalable, and reliable data backbone required for advanced AI systems to operate effectively. These open source technologies are critical for handling the vast amounts of data that agentic AI frameworks rely on to learn, adapt, and make autonomous decisions.
Agentic AI frameworks are designed to create AI systems that act as independent agents, capable of perceiving their environment, learning from it, and making decisions to achieve specific objectives. These frameworks require a data infrastructure that can support real-time data ingestion, processing, and storage at scale. Instaclustr’s platform ensures that these requirements are met with enterprise-grade security, high availability, and 24/7 support, allowing businesses to focus on developing and deploying their AI solutions without worrying about the complexities of managing the underlying infrastructure.
The integration of managed open source services with Instaclustr with agentic AI frameworks unlocks new possibilities for innovation and automation. For example, an agentic AI system designed for supply chain optimization can leverage Instaclustr for Apache Kafka for real-time data streaming and Instaclustr for Apache Cassandra for scalable data storage. This enables the AI system to process live data from multiple sources, adapt to changing conditions, and make autonomous decisions to improve efficiency and reduce costs. By combining Instaclustr’s reliable data infrastructure with the adaptability of agentic AI frameworks, organizations can build intelligent systems that drive smarter decision-making and deliver transformative business outcomes.
For more information: