What are managed PostgreSQL tools?
Managed PostgreSQL tools refer to software applications and platforms designed to simplify the administration, development, and monitoring of PostgreSQL databases, particularly within a managed service environment (e.g., cloud-based managed PostgreSQL offerings). These tools aim to abstract away the complexities of manual database management, allowing users to focus on data and application development.
They are intended to reduce operational overhead, minimize downtime, and improve reliability for organizations that rely on PostgreSQL as their primary data store. Such tools are available from major cloud providers and dedicated platforms, offering database hosting as well as advanced features like monitoring, scaling, and integrated security. By delivering PostgreSQL database services “as-a-service,” they let teams focus on development and business logic.
They are intended to reduce operational overhead, minimize downtime, and improve reliability for organizations that rely on PostgreSQL as their primary data store. Such tools are available from major cloud providers and dedicated platforms, offering database hosting as well as advanced features like monitoring, scaling, and integrated security. By delivering PostgreSQL database services “as-a-service,” they let teams focus on development and business logic.
Managed PostgreSQL tools vs. self-hosted
Self-hosting PostgreSQL means installing and running the database on your own servers or virtual machines. This approach gives full control over configuration, extensions, and performance tuning, but it also requires in-house expertise to handle tasks like upgrades, backups, and high availability. Teams must design their own monitoring, scaling, and disaster recovery strategies, which increases operational complexity and cost.
Managed PostgreSQL tools shift these responsibilities to the provider. Provisioning is typically done in minutes, with automated backups, monitoring dashboards, and scaling options built in. Failover and replication are handled by the service, reducing the risk of downtime. Security patches and version updates are applied automatically, lowering maintenance overhead.
The trade-off is reduced flexibility. Managed services may limit access to certain system-level configurations, restrict unsupported extensions, or impose PostgreSQL performance constraints. Costs are also higher per unit of compute or storage compared to self-managed deployments, but many organizations accept this premium in exchange for reliability and lower operational burden.
Choosing between managed and self-hosted PostgreSQL depends on priorities: control and customization versus speed, simplicity, and reduced maintenance effort.
Related content: Read our guide to PostgreSQL performance
Key features to look for in a managed PostgreSQL tool
Automation and CI/CD integration
Automation is vital for accelerating deployments and reducing manual errors in database management. Managed PostgreSQL platforms should enable automated provisioning, scaling, failover, and routine maintenance tasks like backups and recovery. These automation capabilities ensure consistent performance and reliability as databases grow or as development teams scale up their activities.
Integration with CI/CD pipelines is equally important for modern workflows. Managed tools should offer APIs, command-line interfaces, or native integrations with popular DevOps platforms, enabling teams to automate schema migrations, run database tests, and deploy infrastructure as code.
Cross-platform and cloud-native capabilities
With hybrid and multi-cloud strategies gaining traction, organizations benefit from managed PostgreSQL solutions that can deploy seamlessly across on-premises, public, and private clouds. Look for tools offering broad compatibility with different cloud providers and container orchestration systems like Kubernetes. This flexibility ensures teams can avoid vendor lock-in and orchestrate their databases alongside other cloud-native services.
Cloud-native capabilities also include built-in monitoring, autoscaling, and automated failover that align with modern distributed application architectures. Managed PostgreSQL tools should natively support microservices, serverless, and event-driven patterns, making them suitable for contemporary application development and deployment scenarios.
Extensibility and plugin ecosystems
A rich extension and plugin ecosystem can significantly improve a managed PostgreSQL tool’s functionality. PostgreSQL’s extensibility is one of its strengths, supporting custom data types, functions, and integrations with third-party tools. Look for managed platforms that allow easy enabling of popular extensions like PostGIS, pg_partman, or TimescaleDB without complex manual installation processes.
The ability to develop, deploy, or install custom plugins expands the utility of PostgreSQL to specialized use cases, such as advanced analytics, full-text search, or time-series data management.
Cost efficiency and licensing considerations
Cost is a key factor when evaluating managed PostgreSQL tools. These platforms typically use a consumption-based pricing model, charging for storage, compute, and data transfer. Assess whether the provider offers transparent, predictable billing and supports scaling resources up or down based on demand, helping to control overall expenditures.
Licensing is another consideration: some providers offer open -source PostgreSQL, while others bundle proprietary enhancements or management tools, which may involve additional fees or usage restrictions. Carefully review the licensing terms to avoid unexpected costs or limitations. Cost efficiency should be balanced with the level of support, features, and scalability needed.
Security and compliance support
Security is a primary concern when managing any database, and managed PostgreSQL tools are expected to provide robust security controls. Look for features such as end-to-end encryption, both at rest and in transit, granular access management, and automated security patching. Compliance certifications, such as SOC 2, HIPAA, or GDPR support, are crucial for organizations in regulated industries, ensuring the service provider meets strict data governance standards.
Equally important is audit logging and monitoring, which allows organizations to track access and changes to sensitive data. Managed tools should offer integration with enterprise identity providers, support for role-based access controls (RBAC), and automated vulnerability management.
Learn more in our detailed guide to PostgreSQL management
Notable managed PostgreSQL tools
1. NetApp Instaclustr

Instaclustr offers a fully managed PostgreSQL service, enabling businesses to focus on their applications rather than database administration. With Instaclustr for PostgreSQL, organizations gain access to enterprise-grade capabilities, robust security, and unparalleled support freeing teams from the complexities of managing database infrastructure.
Key capabilities of Instaclustr for PostgreSQL
- Fully managed service: End-to-end management of PostgreSQL clusters, including provisioning, monitoring, maintenance, and scaling.
- Automated backups and updates: Automated backups and seamless updates, ensuring data integrity and up-to-date PostgreSQL software.
- High availability: Minimize downtime, thanks to redundant architecture and failover support that keeps databases running 24/7.
- Performance optimization: Leverage integrated performance tuning and monitoring tools to achieve consistently efficient and reliable database operations.
- Security built-in: Benefit from robust encryption and secure architecture, ensuring data is protected at every layer.
- Integration and support: Seamlessly integrate PostgreSQL with other tools in the tech stack and rely on expert support available 24/7.
- Achieve optimal outcomes for GenAI projects: Enhance AI outcomes with pg_search capabilities and move GenAI projects from pilot to production.

Source: NetApp Instaclustr
2. Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL

Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL is a managed database service that simplifies the deployment and operation of PostgreSQL in the cloud. It automates time-consuming tasks such as installation, patching, backups, and replication, allowing teams to set up production-grade PostgreSQL instances.
Key features include:
- Managed operations: Automates installation, updates, backups, replication, and monitoring to reduce administrative overhead
- Quick deployment: Launches production-ready PostgreSQL databases in minutes through the AWS Console
- Scalable storage and compute: Offers SSD-backed storage with support for Provisioned IOPS and on-demand scaling without downtime
- High availability: Supports Multi-AZ deployments for fault tolerance and Read Replicas for horizontal read scaling
- Data security: Provides encryption at rest and in transit, network isolation with VPC, and key management via AWS KMS
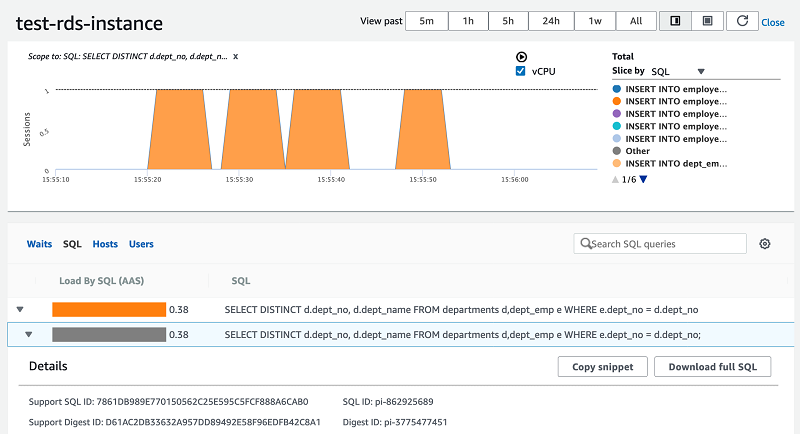
Source: Amazon
3. Microsoft Azure Database for PostgreSQL
Microsoft Azure Database for PostgreSQL is a managed relational database service that enables teams to deploy scalable, secure, and AI-ready PostgreSQL instances in the cloud. Built for mission-critical applications, it offers native support for generative AI use cases, performance optimization through autonomous tuning, and scaling to match workload demands.
Key features include:
- AI capabilities: Use native vector search, embeddings, and the Azure AI extension to build generative AI apps directly within the database
- Autonomous performance tuning: Leverage machine learning to automatically optimize database performance without manual intervention
- Scalable distributed architecture: Support for distributed PostgreSQL enables elastic scaling and high throughput for large datasets and workloads
- Extension support: Includes popular PostgreSQL extensions like PostGIS, PLV8, and Cron, and integrates with frameworks such as Django, Node.js, and Ruby on Rails
- High availability and maintenance: Delivers automated patching, updates, and near-zero downtime scaling for compute and storage
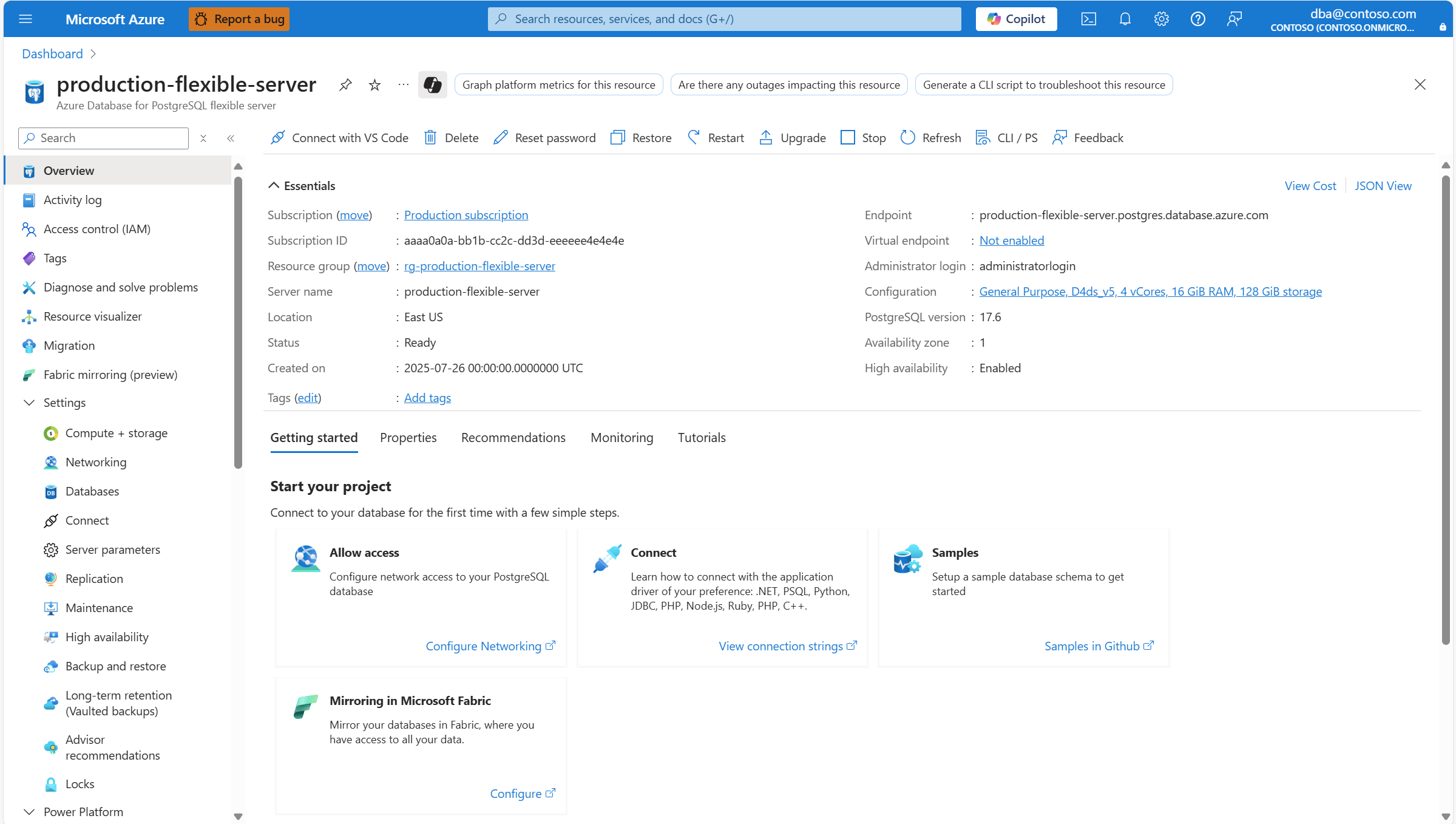
Source: Microsoft
4. Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL is a managed relational database service that delivers the capabilities of PostgreSQL with the scalability of Google Cloud. It automates database provisioning, patching, backups, and failover while maintaining compatibility with standard PostgreSQL tools and protocols.
Key features include:
- Managed PostgreSQL: Handles maintenance tasks such as provisioning, patching, and upgrades, reducing operational complexity
- Global availability: Deploy instances across multiple regions including the Americas, Europe, Asia, and Australia for low-latency access
- High availability and disaster recovery: Offers multi-zone replication with automatic failover, as well as automated and on-demand backups with point-in-time recovery
- Security and encryption: Encrypts data at rest, in transit, and within Google’s internal networks; supports secure access via SSL/TLS and Cloud SQL Auth Proxy
- Standard PostgreSQL compatibility: Maintains support for the PostgreSQL client-server protocol, connectors, and procedural language (PL/pgSQL)
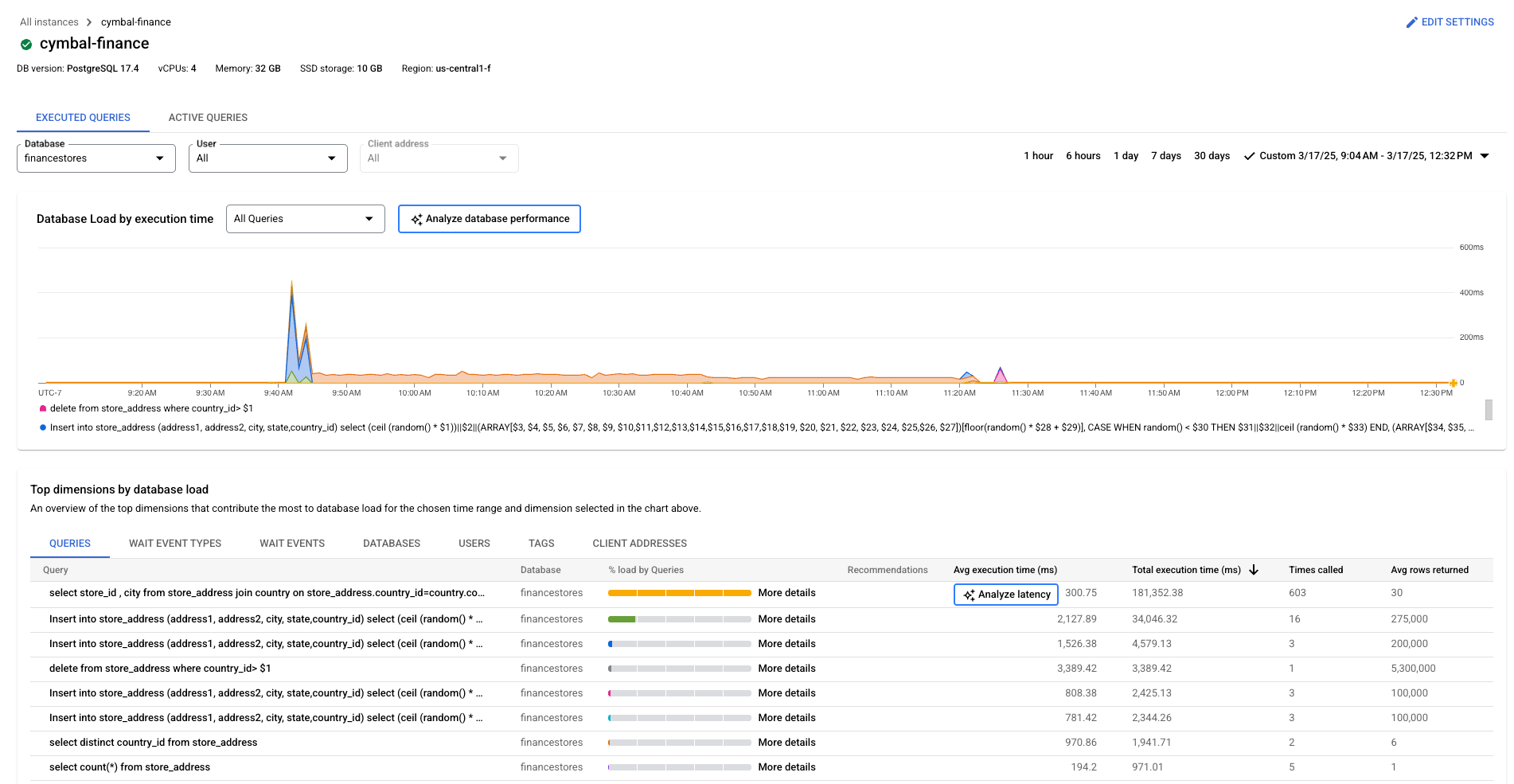
Source: Google Cloud
5. Supabase

Supabase is a managed platform that provides developers with dedicated PostgreSQL databases, real-time capabilities, and API generation without the operational burden. Projects run on scalable PostgreSQL instances, offering portability, extensibility, and compatibility with standard Postgres tooling.
Key features include:
- Dedicated PostgreSQL instances: Every Supabase project runs on its own PostgreSQL database, offering full access and compatibility with existing Postgres workflows
- Portability and migration support: Bring existing Postgres databases or migrate away at any time
- Secure by default: Enforces Postgres row-level security (RLS) with JWT-based access control to tightly govern user data access
- Realtime database: Subscribe to changes in the data via websockets, enabling live updates in client applications with millisecond latency
- Branching support: Sync the database with Git branches to manage previews and test environments, with integration for tools like Vercel

Source: Supabase
Conclusion
Managed PostgreSQL tools simplify database operations by combining automation, scalability, and integrated security into accessible platforms. They help organizations reduce administrative overhead, ensure high availability, and maintain compliance while giving developers more time to focus on building applications. By abstracting infrastructure complexity and offering modern features like CI/CD integration, extension support, and monitoring, these tools enable teams to run PostgreSQL at scale with greater reliability and efficiency.