Connect to an AWS PrivateLink enabled PostgreSQL Cluster
Overview
This page describes the steps needed to connect clients in one VPC to an AWS PrivateLink enabled PostgreSQL cluster in another VPC.
Customers need firstly to setup the AWS VPC Endpoint and the right security groups in the AWS Console. Then secondly configure the PostgreSQL AWS PrivateLink cluster on the Instaclustr Console to connect to the VPC Endpoint.
Once these two steps are done customers can then configure the PostgreSQL client to access the PostgreSQL AWS PrivateLink cluster.
Retrieve Required Cluster Connection Information
- Log into the console, click the created cluster and enter the Connection Info page.
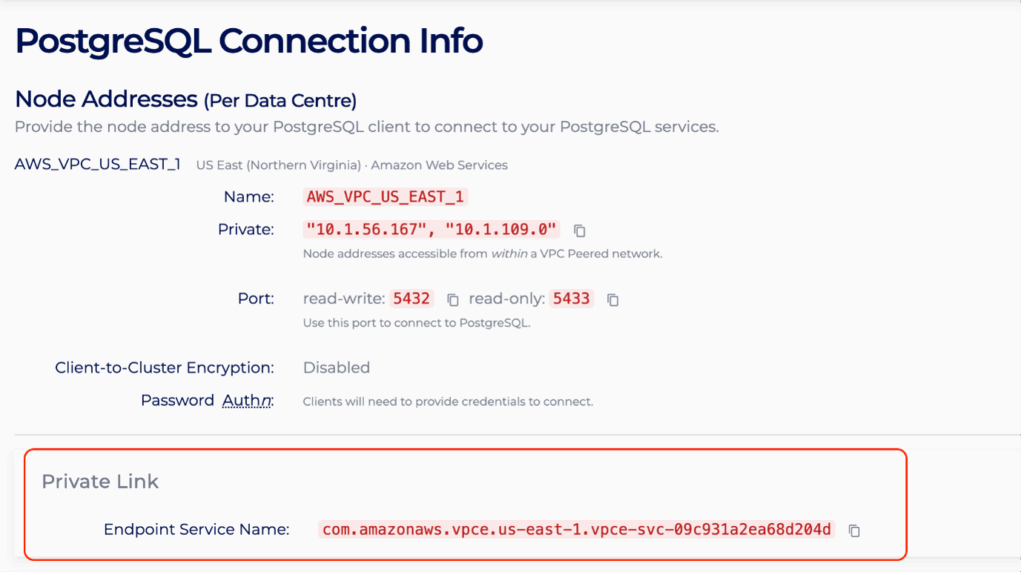
- The Connection Info page contains the specific connection details for PrivateLink. The endpoint created in the next section uses the endpoint service name shown below.
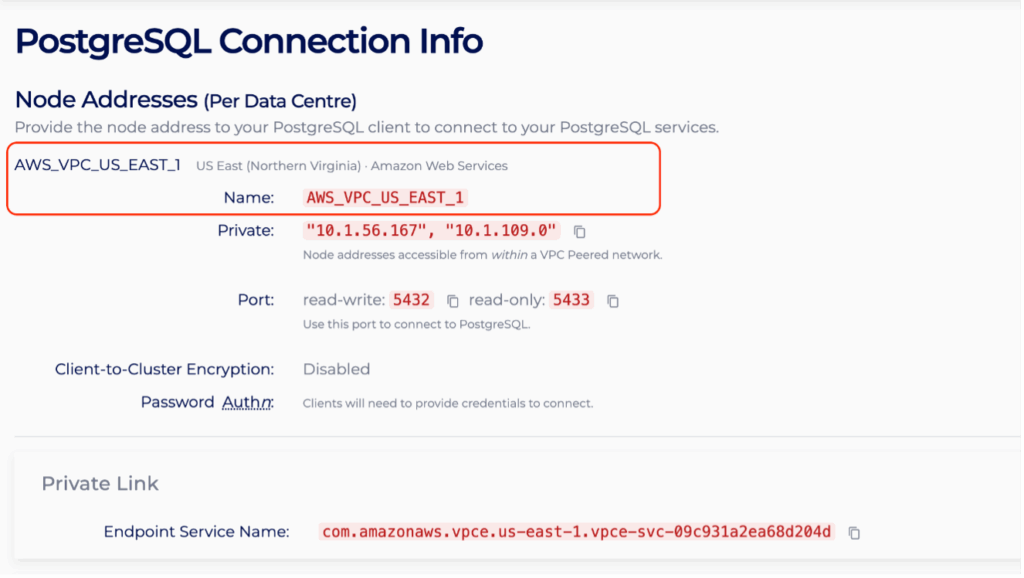
- In the Connection Info page, identify the region of the created PrivateLink PostgreSQL cluster. For instance, the page shows the region is US_EAST_1, hence access to the AWS VPC Endpoint console in the US_EAST_1 region: https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/home?region=us-east-1#Endpoints
- If the PrivateLink PostgreSQL cluster and client are in different AWS accounts, please ensure the AWS Principal of the client AWS account is added to allow cross-account access to the endpoint. For more info, please read Managing Principal ARNs of a PrivateLink PostgreSQL Cluster.
Create Endpoint Security Group
A security group is required to allow traffic from your VPC to the PrivateLink endpoint. Your Instaclustr provided PostgreSQL cluster already has a security group applied to ensure the security of your cluster, but an Endpoint cannot be created without having an associated security group. Therefore, the security group being created here can be as permissive or as strict as you require. These steps will outline the recommended security group configuration.
- In the AWS Console, select the appropriate region for your VPC and navigate to the Security Groups page.
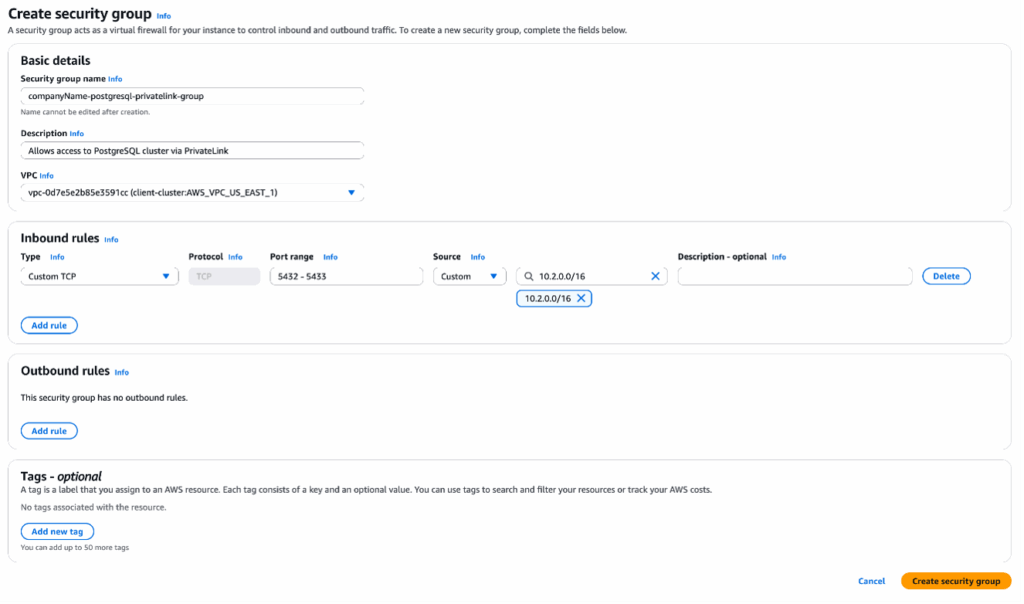
- Click “Create security group”.
- Under the heading “Security group name”, enter a name for the security group. For example, “companyName-postgresql-privatelink-group”. The name cannot be edited after creation, thus it is recommended to use a naming convention which allows easy identification of the PrivateLink endpoint and destination cluster it will be associated with.
- Under the heading “Description”, enter a short description of the security group. For example, “Allows access to PostgreSQL cluster via PrivateLink”.
- Under the heading “VPC”, search for and select the VPC which will connect to the PostgreSQL cluster via PrivateLink.
- Under the Inbound rules heading, click “Add rule”. The rules created here permit traffic outbound from your VPC, inbound to the PostgreSQL cluster over PrivateLink.
- Select Custom TCP in the “Type” field. Enter 5432-5433 in the “Port range” field (n.b. Port 5432 is the PostgreSQL write listener port. Port 5433 is the PostgreSQL read-only listener port. When connecting via PrivateLink, this port is load balanced between all replica nodes in your cluster. These 2 ports will not change and can be verified on your PostgreSQL cluster’s Connection Info page.) Select Custom in the “Source” field, then enter the CIDR of the subnet you will be connecting to the PrivateLink endpoint from (ie. the CIDR within which your EC2 Instance resides). Optionally, add a description in the Description field.
- Click “Create security group”, the security group should be created successfully. Take note of the security group name, as it will be required when creating the Endpoint in the following steps.
Create Endpoint
- On the AWS VPC Endpoint Console page, click Create endpoint.
- On the creation page under Type, select Endpoint services that use NLBs and GWLBs.
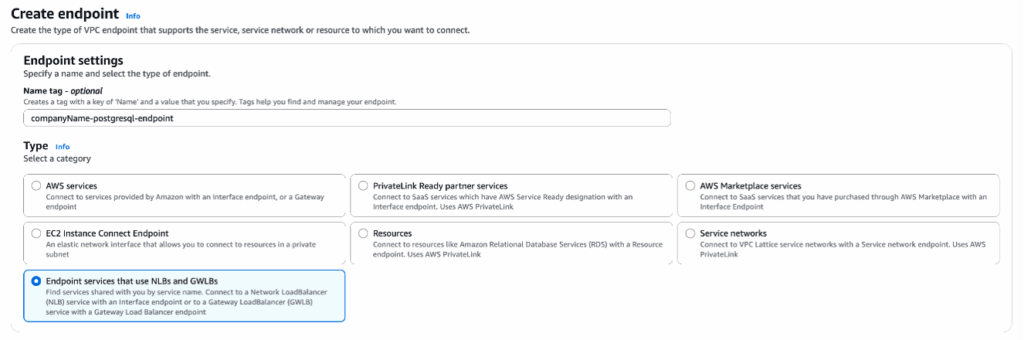
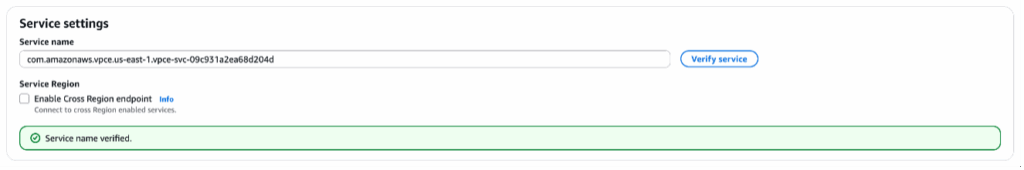
- In Service Settings, paste the endpoint service name from Connection Info page to the Service name field. Click Verify service and a green box will appear.
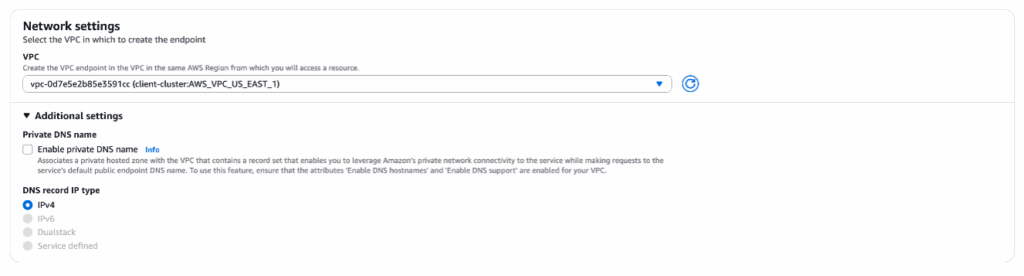
Note: At this point if the Endpoint Service cannot be verified, please make sure you have provided the correct IAM Principal ARN while provisioning the cluster. For more info, please read Managing Principal ARNs of a PrivateLink PostgreSQL Cluster. - For VPC, select the client’s VPC that will connect to the PostgreSQL PrivateLink cluster. Note, the VPC of the client and PostgreSQL PrivateLink cluster should be in the same region as we do not support inter-region access via PrivateLink.
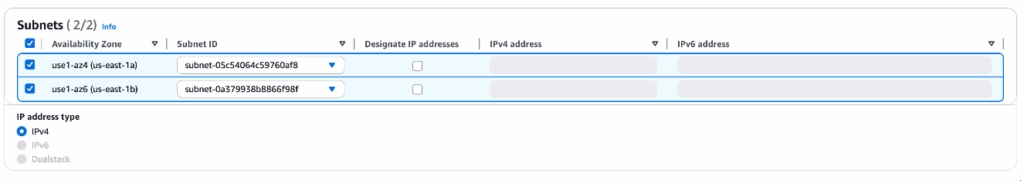
- For Subnets, please select one Subnet ID for each Availability Zone. Please note that we recommend that your clients be located in separate availability zones to support high availability should any one availability zone be unreachable.
- Select the security group that you created earlier and Click Create endpoint at the bottom right of the page.
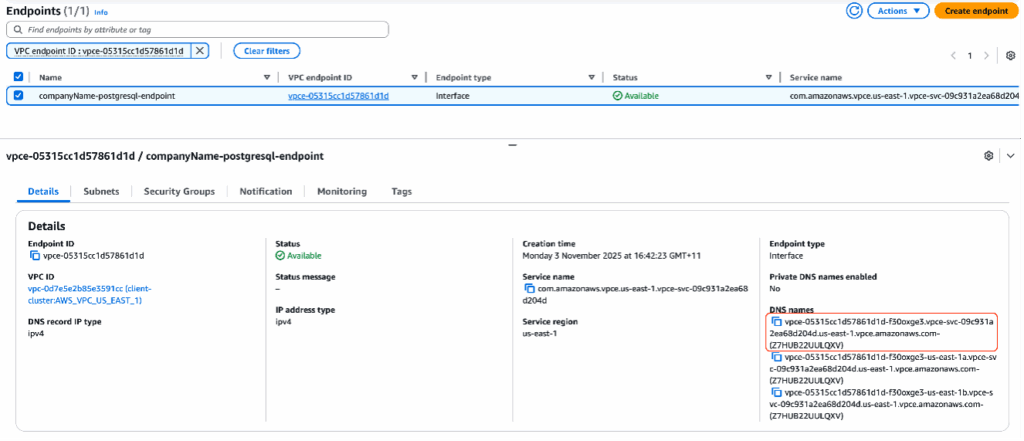
- You will be redirected to the main VPC endpoint page which will specifically show the created endpoint. Once the Status of the endpoint reaches Available, copy the first DNS under the “DNS names”. This DNS name is required for Client connection in the next section
Client Connection
Clients can connect to the PrivateLink-enabled PostgreSQL cluster using the example provided on the Connection Info page. Please refer to Connect to a PostgreSQL Cluster about the general steps required. The key difference is that the host should be set to the first Endpoint DNS.
Note: Clients must be able to retry and establish new connections if existing connections were disconnected.
Additional steps if Client to Cluster Encryption is enabled in the cluster
Set Up the Custom Subject Alternative Names
Currently, Custom Subject Alternative Name for PostgreSQL can only be added via the Terraform provider and Instaclustr API.
- Terraform Provider
Custom SANs must be defined as a list of strings in the data_centre block using the custom_subject_alternative_names attribute.
Example:
1custom_subject_alternative_names = [ "vpce-05315cc1d57861d1d-f30oxge3.vpce-svc-09c931a2ea68d204d.us-east-1.vpce.amazonaws.com"] - Instaclustr API
Custom SANs should be specified as an array of strings in the dataCentres object.
Example:
1"customSubjectAlternativeNames": ["vpce-05315cc1d57861d1d-f30oxge3.vpce-svc-09c931a2ea68d204d.us-east-1.vpce.amazonaws.com"]
Note: Updating custom SAN requires a cluster reload. You could reload nodes via Instaclustr Console or Instaclustr API. For more info, please read Reloading a Node.