Cluster Data Backups
This page describes the automated Snapshot Backup service that is provided to all Instaclustr-managed Cassandra clusters. In addition, this page also describes Instaclustr’s backup functionality on Cassandra Secondary Indexes.
Instaclustr provides two backup services: Snapshot Backup and Continuous Backup. Both backup services transfer backed up data to cloud provider storage (e.g. S3 storage bucket for an AWS cluster) for retention for a period of 7 days. The Continuous Backup service is an optional add-on that allows for more frequent backups to be taken.
Table of Contents
Snapshot Backup
Snapshot Backup is the default backup service. Under Snapshot Backup, all cluster nodes will perform a snapshot backup once every 24 hours. This involves Instaclustr running a nodetool snapshot operation across all keyspaces on the node and then uploading the snapshot files to cloud storage. Node snapshot timing is staggered to reduce the impact of backup operations on the overall cluster performance.
Manual Backup
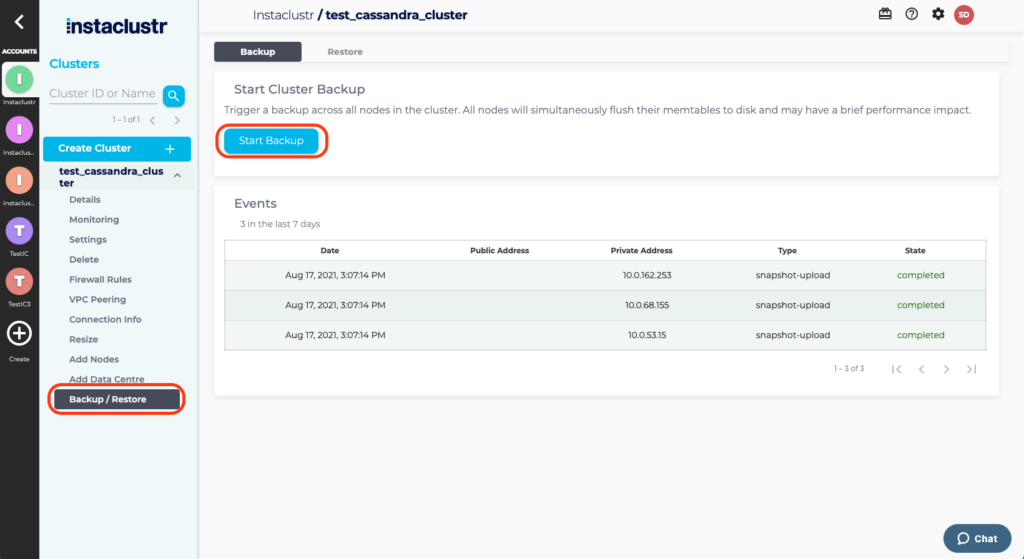
The Instaclustr platform provides a feature to back your cluster manually from the console. Starting a backup will trigger a backup across all nodes in the cluster. All nodes will simultaneously flush their memtables to disk and may have a brief performance impact.
To perform a Manual Backup, click on Backup / Restore under the cluster’s menu on the sidebar.
Then click on the Start Backup button to trigger a backup across all nodes in the cluster. A list of all the backups that have been triggered will be displayed under the Events subsection on this page.
Backups of Cassandra Secondary Index
The Instaclustr backup services backs up any secondary indexes a cluster has to a cloud storage location (e.g. S3 storage bucket for an AWS cluster). The exact location and the file naming convention used for the backed up files depends on the type of secondary index and the version of Cassandra.
- Regular Secondary Index
- Cassandra 2.2 +
Secondary index will be stored as sstables under a separate directory inside their respective tables. The secondary index directory is named as ‘.nameOfTheIndex’. The naming convention of sstable files is, ‘md-#-big-*’, eg. md-1-big-Data.db - Cassandra 2.1.x & Cassandra 2.0.x
Secondary index will be stored as sstables in the same directory of their respective tables. The naming conventions of sstable files are,
For Cassandra 2.0.x,
‘keyspace-table.nameOfTheIndex-jb-#-*’, eg. testkeyspace-testtable.testindex-jb-1-Data.db
For Cassandra 2.1.x,
‘keyspace-table.nameOfTheIndex-ka-#-*’, eg . testkeyspace-testtable.testindex-ka-1-Data.db
- Cassandra 2.2 +
- SASI Index (SSTable Attached Secondary Index)
Another important difference with SASI Index is that if a cluster already has SASI index before the Instaclustr backup service is started, the backup service will not backup SASI index. In such a scenario, the Cassandra service needs to be restarted. If this situation occurs on a production cluster, you can contact our technical support team for assistance.
Naming convention: ‘md-1-big-SI_table_column_idx.db’